FinTech Regulation: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Regulatory Frameworks
Last updated:17 April 2024

Gone are the days when FinTech was considered an unregulated industry. In today’s dynamic financial landscape, with the global FinTech market size reaching approximately $226.71 billion in 2023, the importance of FinTech regulation can’t be overstated.
As the industry continues to innovate and disrupt traditional financial institutions, regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in ensuring customer protection, maintaining stability in financial markets, and managing risks in FinTech activities.
Moreover, FinTech compliance regulations provide a conducive environment for responsible entrepreneurship in the financial sector. When it comes to fair competition, financial regulations set standards for FinTech companies to prevent unfair or deceptive acts, such as money laundering, and promote a level playing field with traditional financial institutions. Last but not least, clear and transparent regulations enhance investor confidence and facilitate international expansion.
We present this comprehensive guide because we understand the challenges of navigating FinTech laws and regulations. It can be especially daunting for startup owners or technical specialists seeking to grasp what they must take into account when developing software for financial institutions. In this article, we'll explore the legal and regulatory landscape of FinTech, delve into compliance nuances, and provide essential insights for financial services businesses.
Key FinTech Regulatory Bodies
FinTech regulatory bodies are entrusted with overseeing FinTech activities and ensuring compliance with relevant FinTech laws and regulations. However, the main complexity surrounding financial regulations arises from the variety of regulatory bodies across different regions.
Specific laws apply in each major region that must be adhered to if the parties are located there. The good news is there is significant overlap in FinTech laws and regulations across different territories. Nevertheless, it’s advisable to thoroughly review them before launching a FinTech company in a particular region.
FinTech Regulatory Bodies in the US
In the United States, several federal regulators and state regulatory bodies are involved in the oversight of banks, federal savings associations, and FinTech companies that provide financial services.
At the federal level:
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): The CFPB is responsible for ensuring that consumer financial services and products offered by FinTech companies are fair, transparent, and comply with federal consumer financial laws.
- The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC): The OCC regulates and supervises national banks, federal savings associations, and FinTech companies.
- The Federal Reserve Board of Governors: The Federal Reserve Board oversees bank holding companies, processes certain payments, and ensures compliance with federal laws.
- The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation: It deals with insured deposits at national banks and credit unions.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): The SEC is one of the federal regulators that regulates the securities markets, including crowdfunding platforms and other FinTech companies offering investment-related financial products, in accordance with federal laws.
- The Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA): The FHFA oversees residential mortgage loans.
- The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council: The US government interagency body is empowered to prescribe uniform principles, standards, and report forms to promote uniformity in the supervision of financial institutions and national banks.
- The Federal Trade Commission: It’s an independent agency of the United States government whose principal mission is the enforcement of civil antitrust law and the promotion of consumer protection.
- Financial Crimes Enforcement Network: This bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury collects and analyzes information about financial transactions in order to combat domestic and international money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes.
- The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC): An independent agency of the US government that protects the public from fraud, manipulation, and abusive practices related to the sale of commodity and financial futures and options.
At the state level:
- State banking departments
- Secretaries of state
- Consumer protection agencies
- State securities commissions and other financial institutions.
FinTech Regulatory Bodies in the UK
In the United Kingdom, the primary strengths in FinTech's progress are policies, regulation regimes, and government programs. According to the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) are responsible for regulating financial firms, including FinTech companies, to ensure they are operating in a safe and sound manner.
FinTech Regulatory Bodies in Europe
In the EU, FinTech regulation is a collaborative effort between various regulatory bodies:
- The European Banking Authority (EBA): The EBA is responsible for ensuring effective and consistent prudential regulation and supervision across the EU banking sector, including FinTech companies offering banking financial services.
- The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA): The ESMA oversees securities markets and investment firms involved in FinTech activities.
- The European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA): The EIOPA regulates the insurance and occupational pensions sectors, and FinTech companies offering insurance-related financial products.
- Individual member states also have their own national regulatory bodies that work in conjunction with the EU authorities to regulate FinTech within their respective jurisdictions. For example, the Federal Financial Supervisory Authority, known as BaFin, in Germany.
Fintech Regulatory Bodies in Other Regions
Across different regions and countries, various regulatory bodies exist:
- Financial Stability Board: It’s an international body that monitors and makes recommendations about the global financial system.
- The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS): The MAS is a leading financial industry regulatory authority, providing a regulatory sandbox for FinTech companies to test their products and services in a controlled environment.
- The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA): The HKMA is responsible for regulating the banking industry in Hong Kong.
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC): The ASIC oversees the FinTech companies offering investment-related products in Australia.
- The Financial Services Agency (FSA) in Japan: The FSA is responsible for regulating the financial services provided by FinTech companies in the country.
It's important to note that the regulatory landscape for FinTech is constantly evolving, with multiple jurisdictions developing new frameworks and guidelines to address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the FinTech industry.
Learn about our expertise in the industry and what we have to offer

Licensing and Registration
Licensing and registration are critical components of the regulatory framework for FinTech companies. These processes ensure that FinTech entities comply with relevant laws and regulations, maintain operational standards, and prioritize consumer protection.
Requirements for FinTech Entities
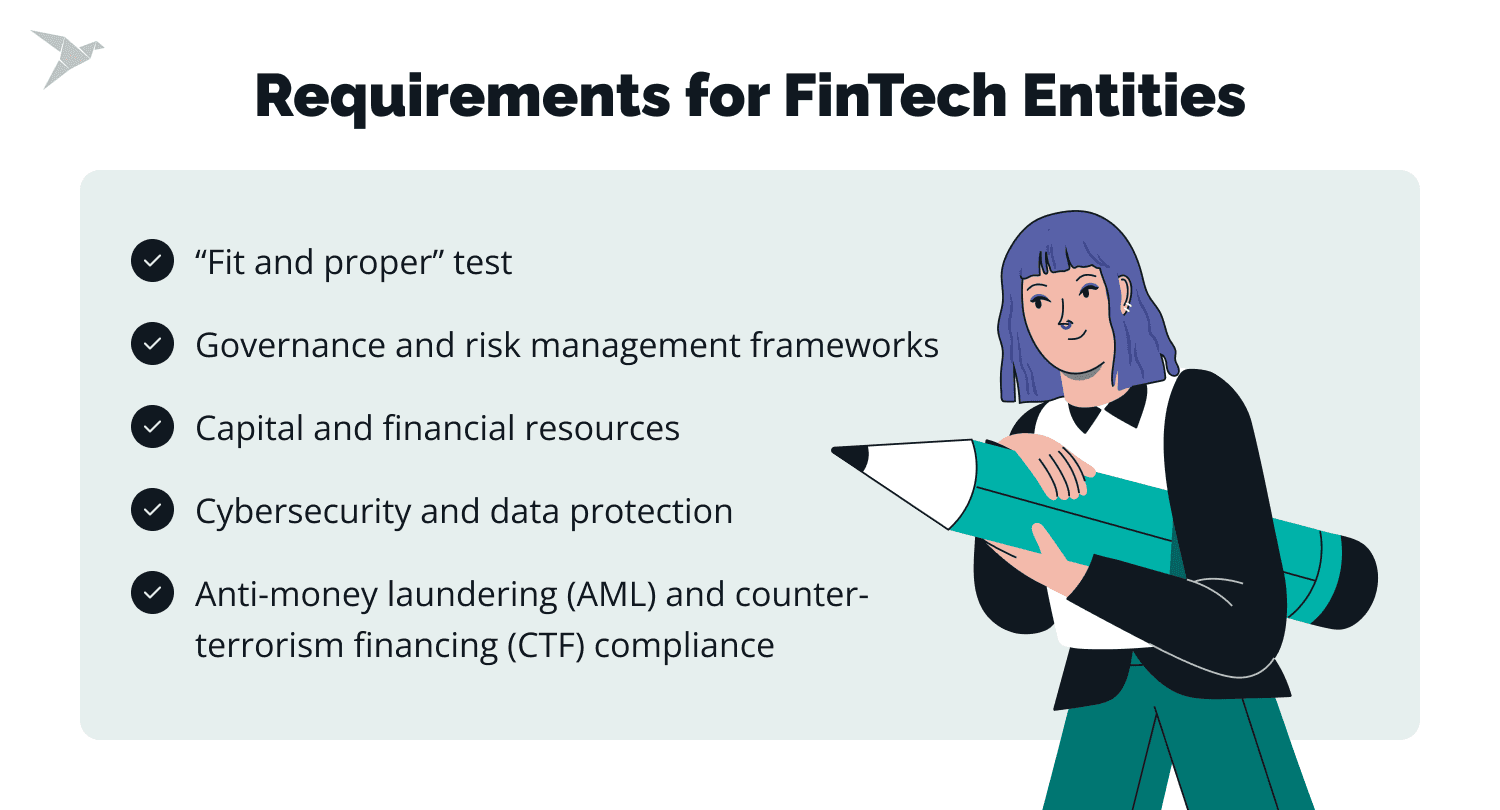
Working with the FinTech sector, we see that the specific licensing and registration requirements for FinTech companies can vary. This variation depends on the jurisdiction, the type of financial services or products offered, and the business model. Among common requirements are:
- Capital and financial resources: FinTech companies need to demonstrate sufficient capital and financial resources to ensure their operational sustainability and ability to meet compliance obligations.
- Governance and risk management frameworks: Robust governance structures, risk management processes, and internal controls are often required to ensure prudent operations and effective oversight.
- Cybersecurity and data protection: Given the technology-driven nature of FinTech, companies must implement strong cybersecurity measures and comply with data protection regulations to safeguard sensitive information.
- Anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) compliance: FinTech entities must have effective AML and CTF programs in place to prevent their services from being used for illicit activities.
- “Fit and proper” test: Key personnel, such as directors and senior managers, need to meet specific "fit and proper" criteria, demonstrating their integrity, competence, and experience.
Navigating the Licensing and Registration Processes
Obtaining the necessary licenses can be a complex and time-consuming process for FinTech companies. It often involves extensive documentation, compliance with requirements, and ongoing monitoring and reporting obligations. To navigate this process effectively, FinTech entities should consider the following strategies:
- Seek legal and regulatory advice: Engaging with experienced legal and regulatory professionals can provide valuable guidance on the specific requirements, documentation, and processes involved in obtaining banking licenses and registrations.
- Participate in regulatory sandboxes: Many jurisdictions offer regulatory sandboxes, which allow FinTech companies to test their financial products and services in a controlled environment with regulatory support and guidance.
- Establish strong compliance frameworks: Building robust compliance frameworks from the outset can help FinTech companies demonstrate their commitment to requirements and facilitate the licensing and registration process.
- Foster open communication with financial regulators: Maintaining open and transparent communication with relevant regulatory bodies can help FinTech companies understand expectations, address concerns, and navigate the process more efficiently.
- Stay updated on regulatory changes: The regulatory landscape is subject to change. Therefore, it's important for FinTech companies to keep abreast of changes in licensing and registration requirements to ensure ongoing compliance.
Consumer Protection Laws
Safeguarding the interests of consumers is the top priority for FinTech entities. That's why regulatory bodies, such as the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US, have implemented consumer protection laws to ensure transparency, prevent unfair or deceptive acts, and protect sensitive consumer data.
Based on our experience, to ensure that FinTech companies operate ethically and treat consumers fairly, they should follow regulations:
- Disclosure and transparency: FinTech entities must provide clear, accurate, and comprehensive information about their products, services, fees, and terms and conditions to enable informed decision-making by consumers.
- Data protection and privacy: Regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), one of the broadest online privacy laws in the US, establish rules for the collection, use, and protection of consumer data.
- Consent and control over data: Consumers must have control over their personal data, with FinTech companies required to obtain explicit consent for data collection and provide mechanisms for consumers to access, rectify, or delete their data as needed.
- Data minimization and retention policies: FinTech companies must only collect and retain the minimum amount of consumer data necessary for their legitimate business purposes, and securely dispose of or anonymize data that is no longer required.
- Complaint handling and dispute resolution mechanisms: FinTech companies must have robust processes in place to address consumer complaints and provide effective dispute resolution mechanisms. In turn, consumers should know the ways to get their money back if they’re affected by a mistake or fraud.
Learn how we built macro-investing app with its own token and reward system
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations aim to prevent the use of financial systems and services for money laundering activities, which involve concealing the origins of illegally obtained funds.
AML Regulations for FinTech
Implementing a robust anti-money laundering program is a must for FinTechs to comply with relevant regulations and mitigate the risk of being exploited for money laundering purposes. Key regulations of the anti-money laundering program for FinTech include:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Verification of the identity of customers, understanding their financial activities, and assessing the potential risks associated with their transactions.
- Transaction monitoring: Analyzing transaction patterns, identifying unusual or high-risk activities, and maintaining detailed records.
- Reporting: Detecting and reporting suspicious activities to the appropriate regulatory authorities and financial intelligence units within specified timeframes.
- Record-keeping: Maintaining comprehensive records of customer information, transactions, and AML program activities for a specified period, allowing for audits and investigations when necessary.
- Risk-based approach: Assessing and understanding unique money laundering risks based on factors such as products, services, customer base, and geographic exposure, and implementing appropriate mitigation measures.
- Training for employees: FinTechs must ensure that their employees are adequately trained to identify and respond to potential money laundering risks.
Strategies for Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance
KYC compliance strategies are all about making sure you really understand who your customers are and what they're up to, without being intrusive. To tackle KYC compliance effectively, FinTech companies can employ a few well-proven strategies.
First, they need robust processes for identifying and verifying customers, which could involve things like biometric authentication, document scanning, and data verification services. They should also adopt a risk-based approach, wherein the level of due diligence and ongoing monitoring is determined by the customer's assessed risk level.
Additionally, FinTech firms can leverage technologies like AI, machine learning, and automation to streamline KYC processes. Partnering with a specialized KYC software provider is another beneficial option. And of course, regular training and awareness programs are crucial for instilling a strong culture of compliance within the organization.
Cybersecurity FinTech Regulations
As FinTech companies heavily rely on financial technology and digital systems, cybersecurity is a critical concern. Regulations are in place to ensure that these firms effectively protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of their systems and services.
FinTech Compliance Regulations and Policies
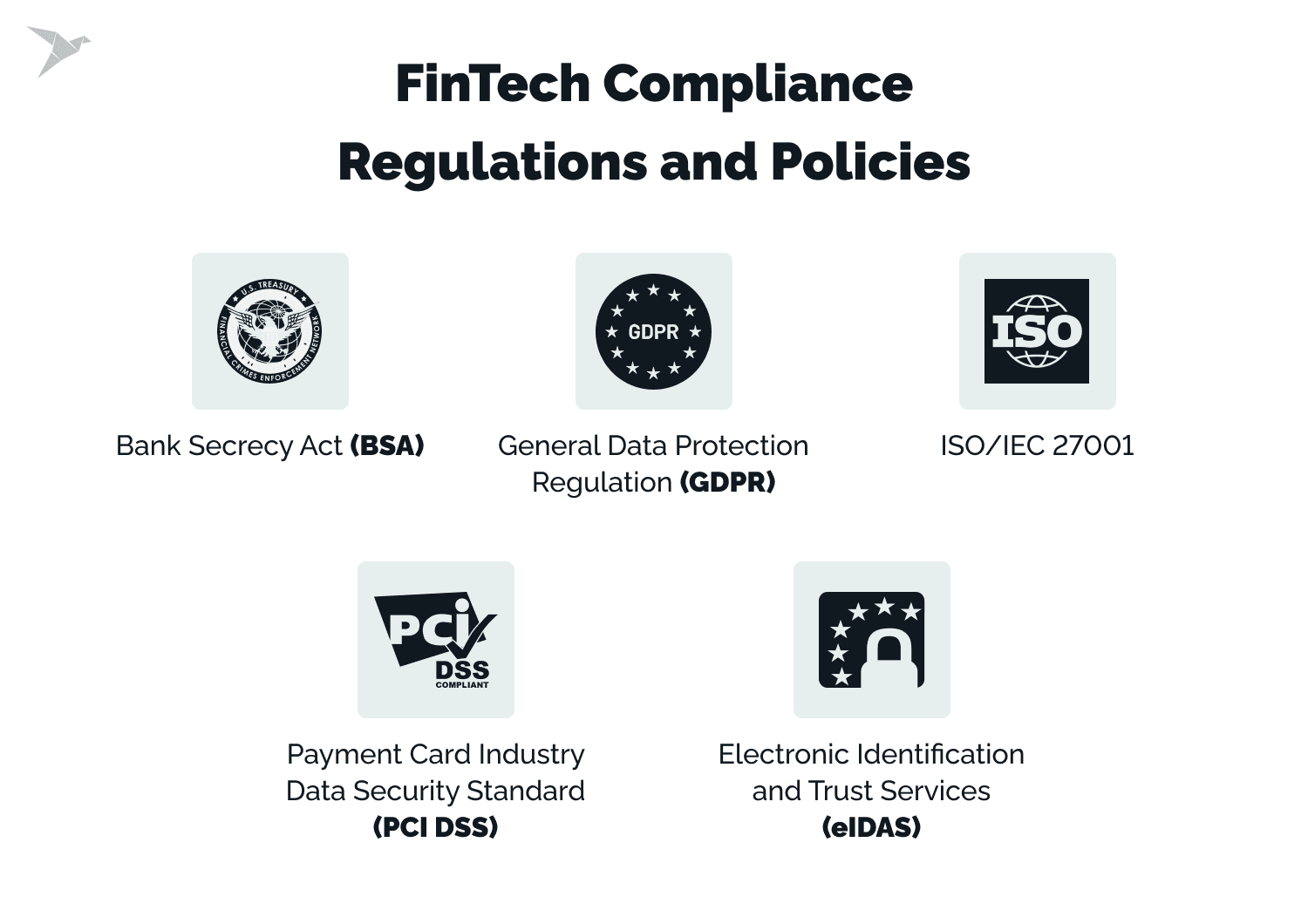
Here are some key cybersecurity regulations and policies that FinTech companies need to be aware of:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This EU regulation sets strict standards for data protection and privacy, and breach notifications.
- Electronic Identification and Trust Services (eIDAS): These regulations establish requirements for secure electronic transactions and data protection.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): This standard, established by major credit card companies, sets requirements for the secure handling of payment card data. Utilizing the PCI Compliance checklist can aid in compliance efforts.
- ISO/IEC 27001: This international standard outlines best practices for information security management systems (ISMS).
- Bank Secrecy Act (BSA): It’s a US law requiring financial institutions in the United States to assist US government agencies in detecting and preventing money laundering.
Compliance Measures for Data Security in FinTech
To address threats and comply with cybersecurity regulations, FinTech companies must implement a variety of measures. This includes strong encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and incident response plans. They also need to ensure that their systems and software are regularly updated and patched to address any vulnerabilities.
Cross-Border Compliance
Navigating cross-border compliance is akin to traversing a maze in the global financial landscape — it's complex and challenging, but ultimately necessary for FinTech companies looking to expand their reach beyond borders.
Challenges in International Operations
One of the biggest hurdles for FinTech firms operating across borders is the lack of harmonized regulations. Every country or region has its own set of rules and requirements, which can vary significantly in areas such as licensing, consumer protection, and AML. Keeping up with these ever-evolving FinTech regulations and ensuring compliance in each jurisdiction can be a daunting task.
Opportunities Unveiled by FinTech
Despite the challenges, the rise of FinTech has also unveiled new opportunities for cross-border financial services. By leveraging technology and digital platforms, FinTech companies can potentially offer their products and services to a global customer base, transcending geographical boundaries. However, capitalizing on these opportunities requires a deep understanding of international regulatory frameworks and a commitment to compliance.
Adhering to Global Regulatory Standards
To navigate the cross-border compliance landscape effectively, FinTech companies must adhere to global regulatory standards and best practices:
- Implementing robust risk management frameworks
- Maintaining transparency
- Fostering open communication with regulatory authorities in different jurisdictions.
Furthermore, FinTech firms may consider partnering with local service providers or establishing a physical presence in key markets to better understand and comply with local laws and regulations. Additionally, participating in FinTech industry associations and regulatory sandboxes can provide valuable insights and opportunities for collaboration on cross-border regulatory issues.
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Solutions
FinTech companies frequently approach us with a common challenge: streamlining and automating compliance processes. Here, RegTech emerges as a game-changer, simplifying the lives of FinTechs. Think of RegTech as the trusty sidekick to FinTech, assisting it in navigating the world of regulations while staying on the right side of the law.
Adoption of RegTech for FinTech Regulatory Adherence
RegTech solutions play a vital role in ensuring compliance for FinTech firms. Here are a few ways in which RegTech transforms regulatory adherence for FinTech companies:
- Automation of compliance tasks
- Real-time monitoring of regulatory changes
- Enhanced risk assessment capabilities
- Improved accuracy and efficiency in reporting
- Integration with existing systems for seamless implementation.
By leveraging RegTech, FinTech companies can reduce compliance costs and mitigate the risks associated with non-compliance.
Challenges in FinTech Regulation and Solutions
FinTech companies push the boundaries of technology and introduce novel products and banking services. However, this rapidly evolving landscape also presents significant challenges in terms of regulatory compliance. Some common hurdles are:
- Adhering to multiple and sometimes conflicting regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. Moreover, keeping up with constantly evolving regulations.
- The unique nature of FinTech products and services may not fit neatly into existing regulatory frameworks designed for traditional financial institutions.
- Grappling with issues related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and AML compliance.
- Meeting requirements can be costly for FinTech startups and smaller firms, requiring significant investments in compliance resources.
These challenges underscore the importance of proactive regulatory compliance strategies and ongoing engagement with regulatory authorities.
Strategies and Solutions for Overcoming Regulatory Hurdles
While navigating FinTech regulation can be daunting, there are several strategies and solutions that companies can employ to overcome regulatory hurdles:
- Stay ahead of regulatory changes by monitoring developments and proactively adapting compliance procedures.
- Leverage RegTech solutions to streamline compliance processes, automate repetitive tasks, and ensure adherence to requirements.
- Engage with regulatory bodies, industry associations, and peer networks to gain insights, share best practices, and advocate for regulatory clarity and consistency.
- Implement risk management frameworks to identify, assess, and mitigate compliance risks, ensuring that regulatory requirements are met effectively.
- Invest in ongoing education and training for employees to ensure awareness of regulatory requirements.
Future Trends in FinTech Regulation
The FinTech industry is experiencing remarkable growth and innovation (the global user base in FinTech is forecast to exceed 3.5 billion in 2024). In turn, regulatory bodies around the world are adapting their approaches to keep pace with the financial sector while ensuring consumer protection, financial stability, and fair competition.
Evolving Regulatory Approaches
As FinTech continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are recognizing the need for more agile and responsive regulatory frameworks. Some key trends are:
- Regulatory sandboxes and financial technology innovation hubs: These controlled environments allow FinTech companies to test innovative products and services while receiving guidance from regulators, fostering responsible financial innovation.
- Risk-based and proportionate regulation: Regulatory bodies are shifting towards risk-based and proportionate approaches, tailoring regulatory requirements based on the specific risks posed by different FinTech activities and business models.
- Harmonization and collaboration: Efforts are underway to harmonize regulations across jurisdictions and promote greater collaboration among regulatory bodies to create a more consistent and cohesive regulatory environment for FinTech companies operating globally.
Future Predictions and Challenges
- Emergence of new technologies: As technologies like distributed ledger technology (DLT), central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and decentralized finance (DeFi) gain traction, regulators will need to adapt and develop new frameworks to address the associated risks and opportunities.
- Data privacy and cybersecurity: With the increasing reliance on data and technology, data privacy and cybersecurity will remain critical areas of focus for regulators, necessitating robust protections and compliance measures.
- Digital identity solutions: The development and adoption of secure digital identity solutions will be crucial for FinTech companies to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations while enhancing customer experience.
- Financial inclusion: Regulators may focus on fostering financial inclusion by encouraging FinTech solutions that provide access to financial services for underserved communities and populations.
- Climate and ESG compliance: Regulatory bodies are expected to place greater emphasis on sustainable FinTech solutions and ensuring compliance with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
- Customer education: Regulators may prioritize initiatives to educate consumers about the risks and responsibilities associated with FinTech products and services. This will foster both informed decision-making and consumer protection.

Conclusion
FinTech is shaking up the financial services game, offering innovative solutions that are making our lives easier and more accessible. But with great innovation comes great responsibility, and that's where regulations come into play.
So, whether you have a FinTech startup or a big FinTech company, it's crucial to stay informed, proactive, and agile in your compliance efforts. Keep your finger on the pulse of regulatory developments and leverage innovative solutions to comply with FinTech laws and regulations.
FAQ
Why is understanding FinTech regulations important for industry professionals?
Understanding FinTech regulations is crucial for industry professionals to ensure compliance in the financial sector, mitigate risks, and operate within legal boundaries. It helps protect consumers, maintain financial stability, and foster trust in the industry.
Who are the key regulatory bodies overseeing FinTech?
Key regulatory bodies include the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), European Banking Authority (EBA), and national regulators in various jurisdictions.
WWhat are common challenges in FinTech regulation, and how can they be addressed?
Common challenges include navigating complex regulations across jurisdictions, dealing with regulatory uncertainty for novel products/services, data privacy, cybersecurity, and AML compliance. Among effective strategies to address these challenges are robust compliance frameworks, RegTech solutions, industry collaboration, and open communication with regulators.
What are the future trends anticipated in FinTech regulation?
The future trends are expected to include agile and responsive regulatory approaches, risk-based and proportionate regulation, regulatory harmonization across jurisdictions, emphasis on data privacy and cybersecurity in the financial system, and promoting financial inclusion and sustainability.


















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy