How To Build a Successful Cloud Security Strategy [Updated]
Last updated:1 February 2026
![How To Build a Successful Cloud Security Strategy [Updated]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ftm-bucket-for-images.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com%2Fcover_Cloud_Security_1_f965643204.png&w=2048&q=100)
Over 90% of companies store their data in cloud environments today. This fact has caused an increased demand for a comprehensive cloud security strategy.
The cloud makes scaling easier. It can also make risk harder to see. Access grows quietly. Services multiply. A single misconfigured storage bucket or overly broad permission can expose data without anyone noticing. On top of that, responsibility is shared with the provider, which often leaves gaps in ownership, monitoring, and incident response.
Over time, poorly designed cloud security strategies can lead to data breaches (which is $4.35 million per breach on average, according to IBM) and financial or reputational losses. We are ready to help you avoid these by sharing our practical recommendations on building a successful strategy.
Our guest expert, Julia Chotkiewicz, a competent cloud security engineer, contributed to this post by sharing her perspective and tips on what organizations must consider while building their cloud security strategy. Keep reading to explore Julia’s insights and recommendations gained over the years of practice.
In this article, we explain what a cloud security strategy is, what it must include, the best practices for cloud security, and where organizations most often face challenges.. You’ll also get a practical, step-by-step approach to building a strategy that holds up in real cloud environments, plus a list of tools experts use to strengthen cloud security. The topic is relevant because cloud adoption keeps growing, and so does the blast radius of small mistakes.
Let’s start!
Key Takeaways
- Cloud environments change fast, so security needs clear ownership, visibility, and enforced controls.
- A cloud security strategy is most valuable when it standardizes access, data handling, and accountability.
- IAM is the main control point in the cloud because one over-permissioned account can expose multiple services.
- Encryption and data classification limit impact, so data protection should be a baseline rather than an optional layer.
- Continuous monitoring is essential because static controls won’t catch misuse or configuration drift in time.
- Governance and compliance work best with automation, since manual reviews don’t scale.
- Shared responsibility confusion is a common root cause of cloud exposure.
- Cloud security improves through assessment, visibility, governance, and continuous optimization rather than a single implementation phase.
What Is a Cloud Security Strategy?
A cloud security strategy is a complex approach that consists of policies, practices, and technologies intended to protect cloud environments, applications, and data against cyber threats. It focuses on the specific challenges of cloud computing and measures for protecting cloud infrastructure and data.
For organizations that need support aligning their strategy with their cloud architecture, our cloud consulting services provide the required guidance.
Cloud security deserves special attention because cloud environments change fast and rarely stay “neat.” Resources can be created, updated, or removed in minutes. Access is spread across employees, contractors, vendors, and automated services. Data can reside in multiple regions and services simultaneously. Without a clear strategy, security becomes a series of isolated fixes that don’t hold up at scale, and small gaps can become a real business risk.
A robust cloud security strategy helps businesses:
- Integrate the most appropriate and cost-effective tools and practices
- Smartly manage multi-cloud environments
- Minimize the risks of insider threats and external attacks
- Protect sensitive data stored on the cloud
- Stay compliant with regulatory requirements
- Smoothly implement security practices without disrupting business operations
What makes a cloud security strategy important is that it clarifies ownership. That matters in cloud environments, where the provider secures the underlying infrastructure but the customer remains responsible for configuration, access, and data handling. When responsibilities aren’t explicit, controls are missed or duplicated, and security decisions depend on assumptions rather than rules.
For companies operating in regulated industries, this approach helps maintain consistent controls, supports audit readiness, and reduces the risk of costly compliance gaps. For organizations using multiple cloud providers, it helps maintain the same security standards across platforms and reduces blind spots caused by different defaults, tools, or identity models.
In a nutshell, a cloud security strategy integrates required security objectives with business goals, which enables organizations to rely on cloud computing with minimal risks.
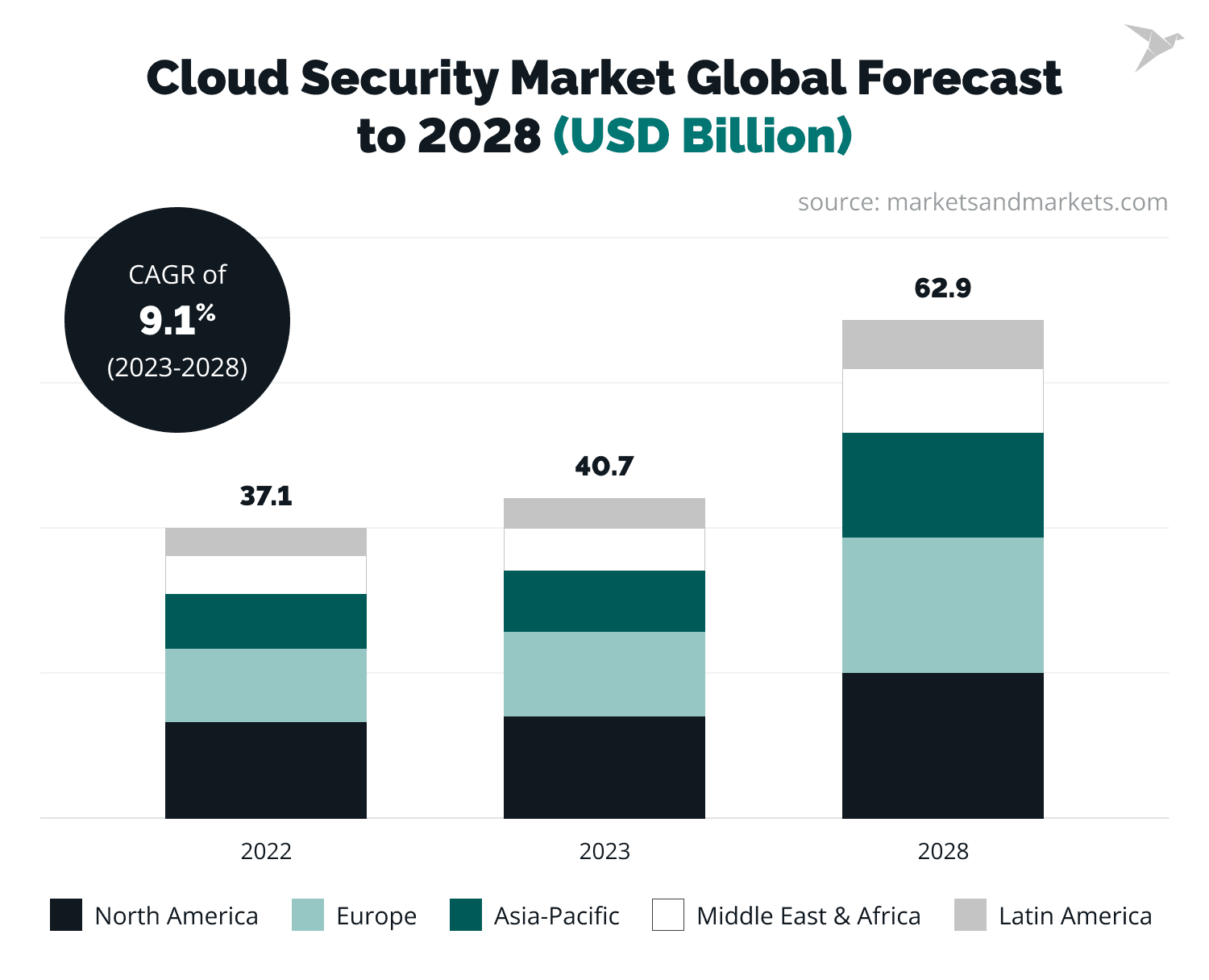
The numbers prove that the cybersecurity market is growing rapidly. Thus, the global cloud security market is predicted to reach $62.9 billion by 2028.
Why Is a Cloud Security Strategy Critical for Modern Businesses?
A cloud security strategy is critical because it strengthens risk management, helps secure sensitive data, and keeps cloud operations stable as environments become more complex and regulated. Without it, security decisions become fragmented, reactive, and hard to scale. Below, we’ll look at why this strategy matters in practice and where it delivers the most value.
It reduces the real cost of security failures
Cloud incidents rarely stop at technical damage. Data exposure can trigger legal action, regulatory penalties, customer churn, and long-term brand erosion. A clear security strategy helps prevent these outcomes by setting consistent rules for how cloud resources are configured, accessed, and monitored, reducing the chance that small oversights escalate into major incidents.
It brings control to dynamic cloud environments
Cloud infrastructure changes constantly. As cloud usage grows, so does your attack surface across cloud services, user accounts, and fast-changing workloads. A strategy provides guardrails, such as a cloud governance framework, so security keeps pace with change instead of falling behind or becoming inconsistent.
It supports compliance without slowing the business
For companies operating under regulatory requirements, cloud security is closely tied to compliance. A strategy aligns security practices with legal obligations from the start, making audits less disruptive and reducing last-minute remediation. This is especially important when data moves across regions or between cloud providers.
If your organization is dealing with constant cloud change, compliance pressure, and limited security bandwidth, TechMagic’s cloud security services can help you set up consistent controls without slowing delivery.
It protects business-critical data and workloads
Not all data carries the same level of risk. A cloud security strategy helps organizations focus protection where it matters most, including cloud data tied to customers, revenue, and core operations. This improves resilience and limits impact if a threat gets through.
It enables safer multi-cloud adoption
Using multiple cloud providers can improve flexibility and resilience, but it also increases complexity. A strategy helps enforce the same security standards across environments, which reduces gaps caused by different defaults, tools, or access models.
What Are the Core Pillars of a Cloud Security Strategy?
Every robust cloud security strategy must be holistic and involve several core components that work together. Each pillar addresses a different layer of risk, from who can access cloud systems to how quickly an organization can respond when something goes wrong.
In practice, these pillars define what is necessary like for cloud security implementation and make security actions repeatable. They also give you a cloud security workflow you can audit: who gets access, how data is protected, what gets monitored, and how incidents are handled.
Let’s look at each pillar and why it matters.
Identity and access management (IAM)
Effective IAM is an essential component of any cloud security strategy. What is its main function? IAM controls who (users, roles, and services) can access which cloud resources and under what conditions. It ensures permissions follow the principle of least privilege, which means all users, roles, and resources receive specific permissions based on job responsibilities that prevent exposure to sensitive areas and reduce the risk of privilege escalation attacks.
Thus, only authorized users and applications can access certain cloud resources, thereby mitigating risks such as stolen credentials, overly broad permissions, and privilege escalation.
In simpler words, the right people access the right resources. IAM controls identities and permissions to reduce the risk of data breaches and insider threats. For example, a marketing manager mustn't have access to financial data.
Key detail that often gets missed: IAM is not only “human users.” It also covers service accounts, APIs, CI/CD identities, and temporary roles. These identities often have broad access by default, so tightening them has a direct impact on reducing breach risk.
Multi-factor authentication and single sign-on methods add extra levels of data security. Such tools as Okta, Azure AD, or AWS IAM help centralize IAM and integrate features like conditional access policies, which restrict access based on device type, location, or risk level.
Learn how threat modeling and attack emulation can protect your AWS environment

Data protection and encryption
Safeguarding data in cloud environments must be a permanent priority, so it is a vital pillar of implementing a cloud security strategy. Its goal is to keep cloud data protected even if access controls fail. Organizations must protect data at rest with strong encryption algorithms, for example, with AES-256.
As for securing data in transit, it is possible with protocols like TLS 1.2 or higher. For instance, encrypting sensitive customer data stored in Amazon S3 guarantees that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable. This mitigates risks related to data exposure, interception, and misconfiguration.
It is also a good idea to use data classification to prioritize sensitive information. Implementing tokenization methods helps replace sensitive fields with unique identifiers in databases, particularly for industries like finance and healthcare. For example, in payment processing, tokenizing credit card numbers minimizes the risk of exposure during a breach. TechMagic offers comprehensive managed cyber security services to protect your data stored on cloud platforms.
Continuous monitoring and threat detection
The next pillar is monitoring cloud environments, which is vital for detecting and eliminating suspicious activities and other security risks. Its purpose is early detection and fast containment. Tools like AWS GuardDuty, Azure Security Center, or Google Chronicle help monitor user activity, application behavior, and network traffic. This pillar mitigates risks such as compromised accounts, malicious activity, and abnormal access to cloud resources.
Behavioral analytics is a vital element. For instance, if an employee usually logs in from Los Angeles but once gets access to the system from a new location in another city or country, the system marks this as a potential security incident. We suggest automating responses with solutions like SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) to contain threats quickly. This matters in cloud environments because threats can spread fast across connected services.
Compliance and governance
This pillar of an organization's cloud security strategy refers to the fact that every organization must align its cloud security measures with relevant regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, etc. An effective practice here is to establish a governance security framework that incorporates these standards and regularly audits cloud configurations to ensure compliance.
The main goal of this pillar is consistent enforcement of security rules and audit readiness. This mitigates risks of non-compliance, configuration drift, and inconsistent controls across environments.
What can help with this? Tools like Prisma Cloud or Microsoft Defender for Cloud help automate compliance checks. They compare cloud environments against industry benchmarks, such as CIS or NIST frameworks. For instance, these tools can alert employees to misconfigured storage buckets that could potentially lead to data exposure.
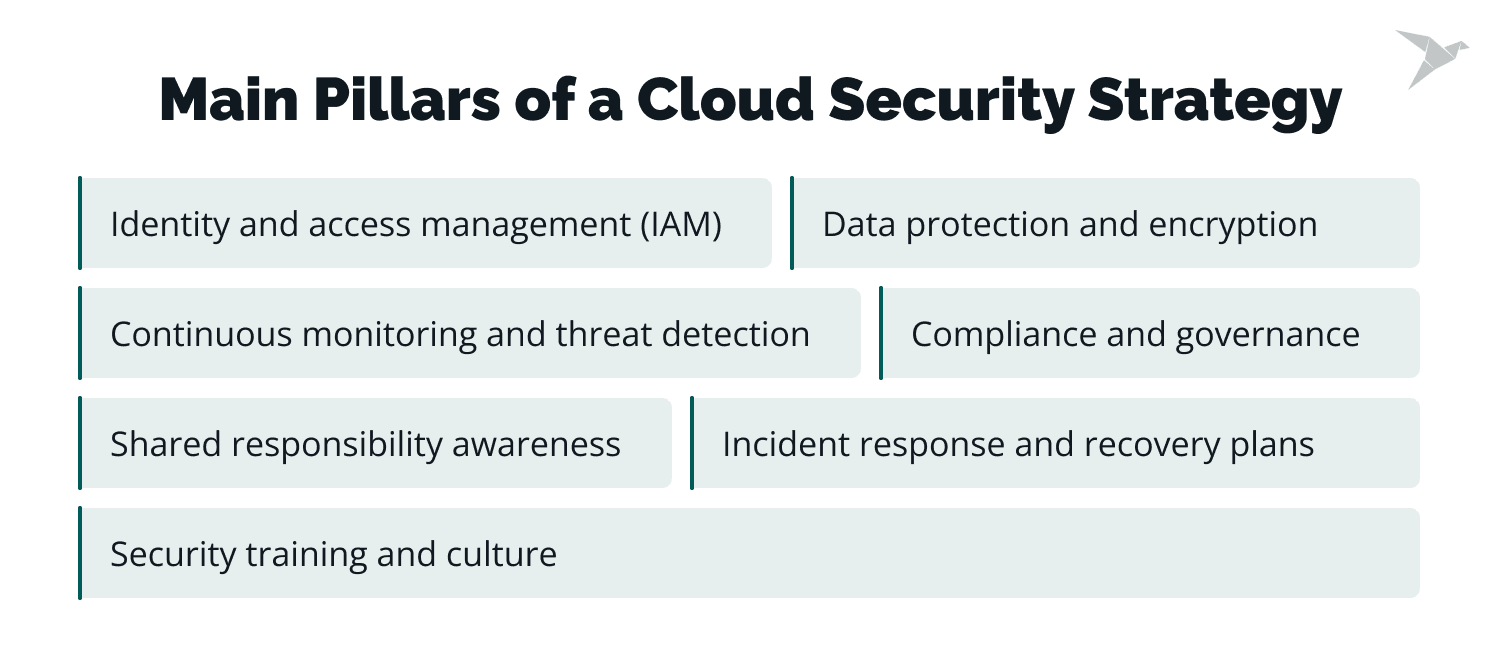
Shared responsibility awareness
An effective cloud security strategy must include implementing shared responsibility awareness. The shared responsibility model is when the cloud provider protects the infrastructure, but customers take responsibility for their applications, data, and configurations. Its objective is to prevent security gaps caused by wrong assumptions about who secures what. Misunderstandings of this model often result in vulnerabilities.
For instance, while AWS secures its data centers and network, customers must configure security groups and encryption for their workloads. It is vital to document roles and responsibilities across teams and conduct regular reviews to ensure no gaps are left unaddressed. This mitigates risks caused by unowned controls, missed configurations, and inconsistent security ownership.
One of the most common mistakes organizations make when it comes to cloud security is an over-reliance on the default settings and features provided by cloud providers. While they offer some security measures, default configurations may not be sufficient to ensure full protection. This is why the shared responsibility model was created, which outlines the division of responsibility between the cloud service provider and the client, meaning us. – Julia Chotkiewicz, Cloud Security Engineer
Incident response and recovery plans
Making a comprehensive incident response and recovery plan specific to cloud environments is a necessary part of a security strategy. How does it work? You need to simulate disaster recovery scenarios to reveal potential weaknesses and refine response readiness times. The purpose is to reduce impact and recovery time during incidents, which mitigates risks such as prolonged downtime, data loss, and incomplete investigations.
For example, setting up automated failover for critical applications using tools like AWS Elastic Load Balancer or Azure Site Recovery. You need to ensure that backups are encrypted and stored redundantly across multiple geographic locations. All these can enable rapid recovery in case of data loss or ransomware attacks.
Security training and culture
Even the best technical defenses can fail without employee awareness. That's why it is necessary to include employee training in the security strategy. Regular security training programs must include phishing simulation exercises and secure development practices, especially for DevOps teams. The main goal of training is to reduce human-driven risk that can bypass technical controls, such as phishing, credential mishandling, and accidental exposure of cloud resources.
It is important to encourage employees to acquire a security-first mindset. For example, providing rewards for spotting and reporting security risks can help create a proactive culture. Also, a good idea is to use platforms like KnowBe4 as they help engage security awareness training and track progress over time. Check Cybersecured.team, a hands-on cybersecurity education platform for businesses, to learn more about security awareness, secure coding, cloud and application security, and secure UX design.
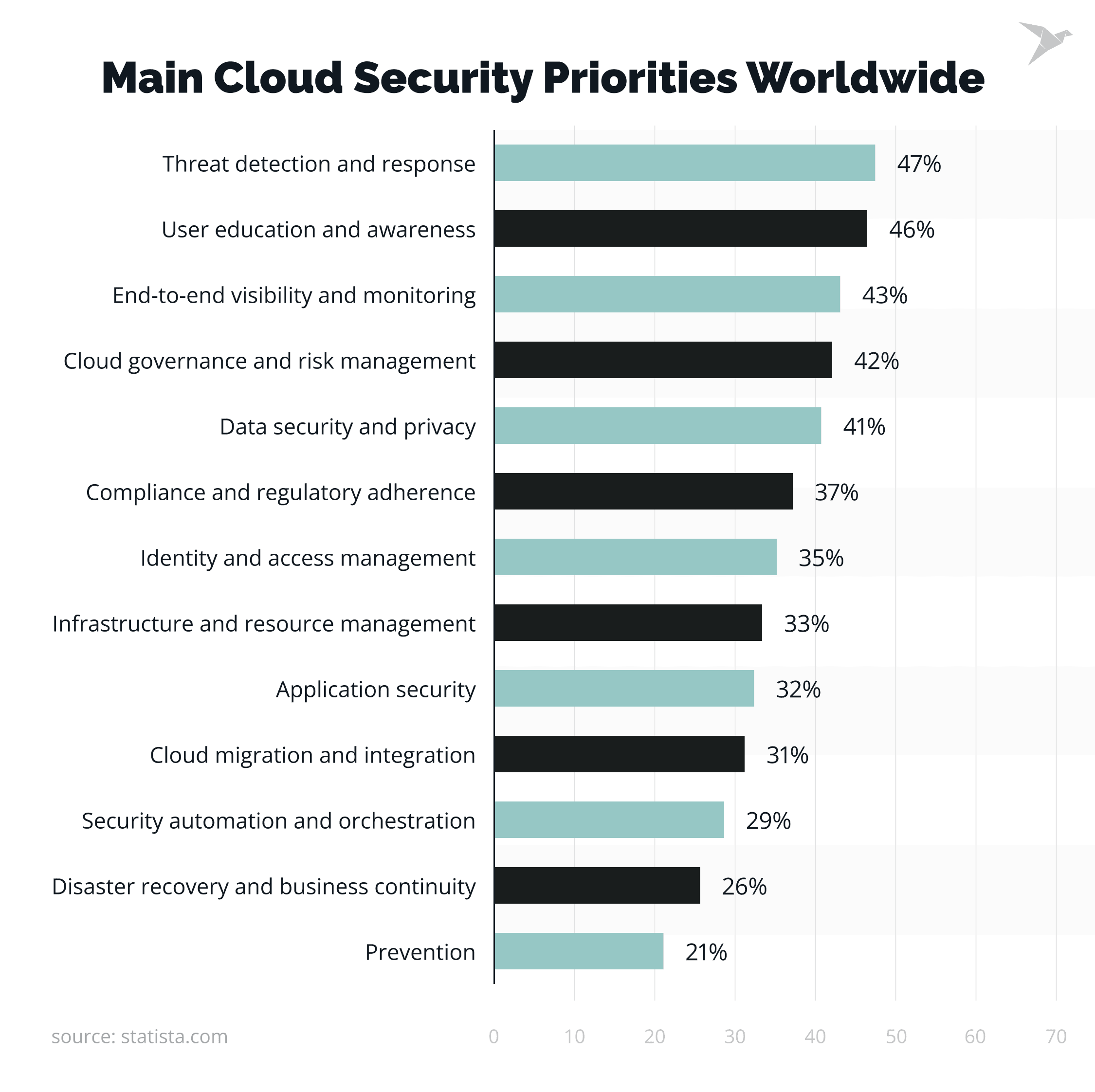

What Are the Biggest Challenges in Building a Cloud Security Strategy?
The biggest challenges in developing a cloud security strategy come from complexity, speed, and shared ownership in cloud environments. These challenges create real risk when security controls can’t keep up with how cloud infrastructure is used and changed. Below are the most common challenges and their solutions.
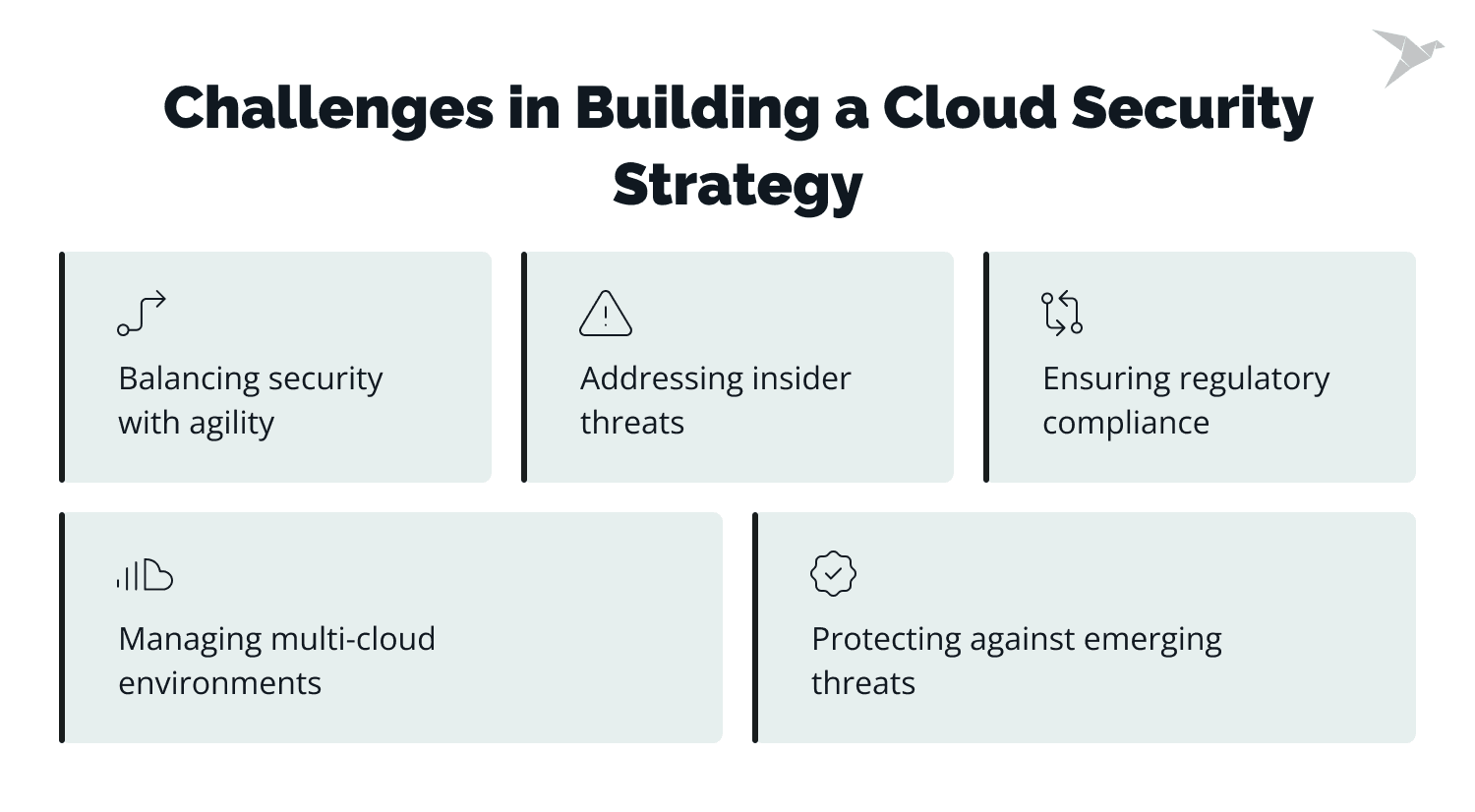
Challenge 1: Managing multi-cloud environments
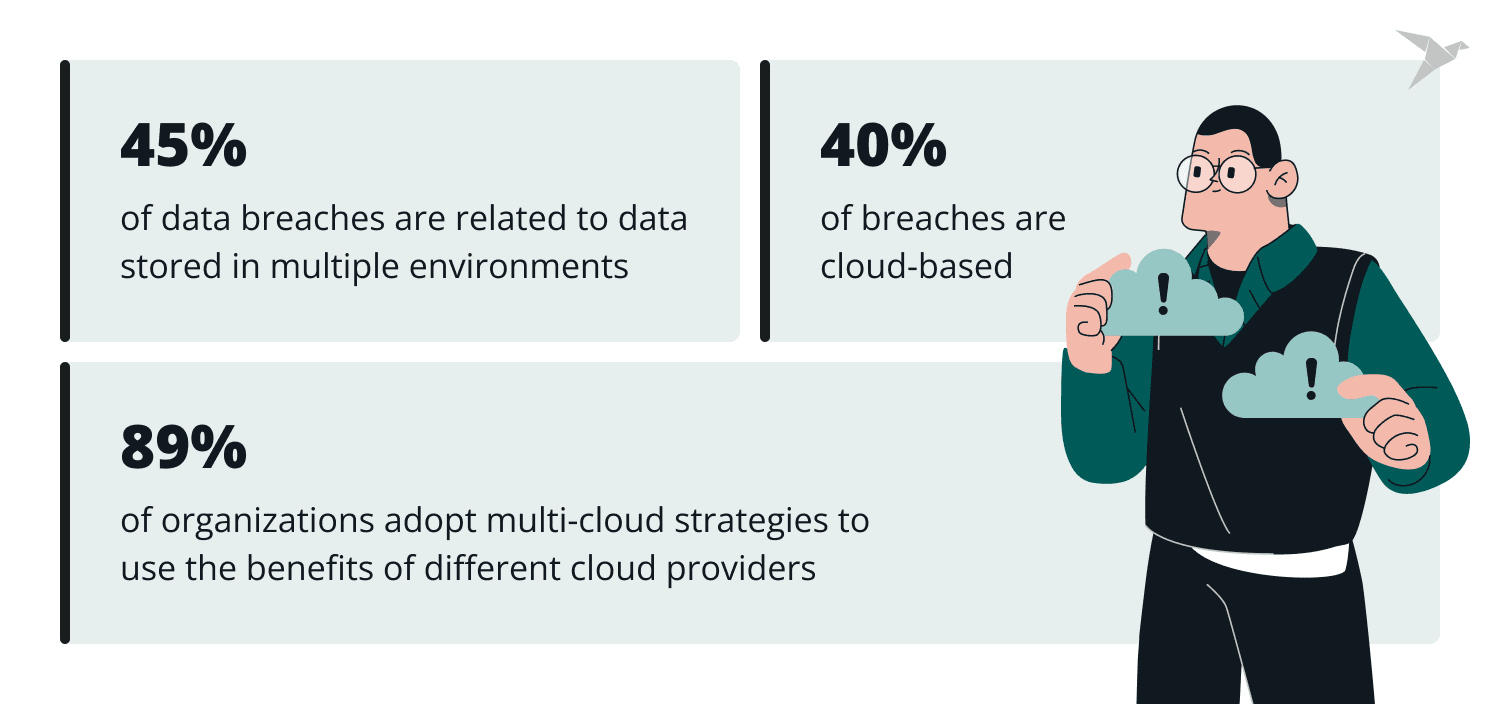
89% of organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies to use the benefits of different providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, etc). A multi-cloud strategy contributes to flexibility, but, at the same time, it causes challenges in managing multiple security policies, configurations, and monitoring across different platforms. This happens because each cloud provider has its own security model, defaults, tooling, and terminology, which makes consistency difficult to maintain.
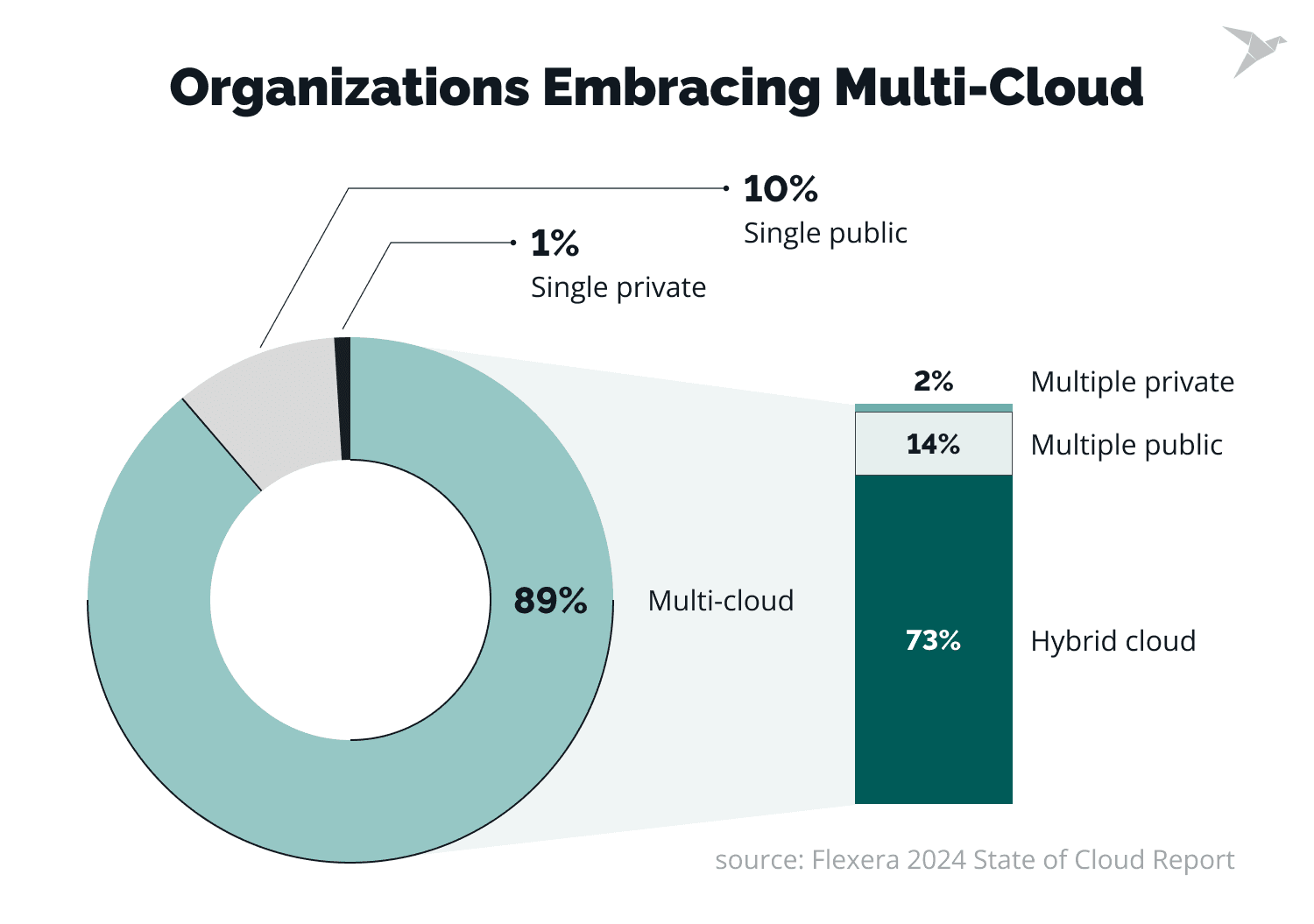
IBM reported that 45% of breaches are cloud-based, and 40% of data breaches are related to data stored in multiple environments. The risk of misconfigurations also grows, which is the primary reason for cloud breaches.
For instance, a company using AWS for data storage and Azure for application hosting may face discrepancies in IAM policies between the two platforms. Over time, these differences make it harder to track who has access to what and why.
To address this, centralized security management platforms like Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs), or Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) can help maintain visibility and consistency. Tools such as Prisma Cloud, Wiz CNAPP, Datadog CSPM, and Lacework can spot misconfigurations across multiple cloud platforms and ensure compliance.
One of the biggest challenges is the lack of a unified approach to managing security across different cloud environments. The best advice for companies transitioning to multi-cloud environments is to ensure consistent security policies across all clouds. This includes standardizing authentication, encryption, and incident response procedures across all platforms to avoid gaps in security. Using cross-cloud security management tools, such as CSPM and SIEM, can help enforce these policies consistently and ensure that the environment will be less vulnerable. – Julia Chotkiewicz, Cloud Security Engineer
Challenge 2: Balancing security with agility
Security measures that are overly restrictive can slow down development and disappoint teams looking for faster deployment. At the same time, insufficient security can pose a vulnerability to the company. This challenge exists because cloud platforms make it easy to deploy quickly, while security controls are often added later or bypassed under delivery pressure.
For example, a development team pressured to release a new feature may ignore security checks, which leads to potential gaps. These gaps often surface later as exposed services, hard-coded secrets, or overly permissive access.
The best solution here is embracing the DevSecOps approach, which integrates security into the development lifecycle from the very beginning. Approaches like Infrastructure as Code (IaC), using Terraform and AWS CloudFormation, provide secure and fast deployment as they implement security configurations into the code. In addition, tools like Snyk and Checkmarx can scan code for vulnerabilities during development to maintain both speed and security.
Understanding the difference between DevSecOps vs DevOps is crucial for companies that want to balance development speed with robust security practices.
Challenge 3: Ensuring regulatory compliance
Organizations that work across multiple regions often encounter varying regulatory frameworks while maintaining a model of shared responsibility for cloud security. This challenge arises because compliance requirements must be enforced across dynamic cloud resources that can change daily.
Non-compliance with these requirements may lead to severe fines and reputational harm, with 4.88$ million being the average global cost of a data breach in 2024. For example, a healthcare organization using cloud storage must ensure compliance with HIPAA, which requires strict data encryption and role-based access controls.
Mapping compliance requirements to cloud services is of high importance. Most major cloud providers ensure compliance tools, such as AWS Artifact for audit reports and Azure Compliance Manager for tracking regulatory adherence. Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools can additionally support compliance with regulatory requirements for delicate data.
Challenge 4: Addressing insider threats
Internal threats, both intentional and accidental, represent a significant risk. They can compromise confidential data, disrupt operations, or create security vulnerabilities. For example, an employee can accidentally share access credentials and make an organization vulnerable to attacks. In cloud environments, insider impact is amplified because a single account can access multiple services and regions.
As mentioned in the previous section, a good solution can be robust IAM with least-privilege access controls. It ensures that users have only the permissions necessary for their roles. Additionally, user behavior analytics and anomaly detection tools like Splunk or Exabeam can track unusual activities. And, of course, regular employee training on security best practices further reduces the chance of negligence.
We’ll share the best tools, techniques, and real-world insights to keep your AWS environment locked down.

Challenge 5: Protecting against emerging threats
New cyber threats appear to exploit vulnerabilities in cloud environments every day. These are sophisticated ransomware attacks, which target cloud backups, or supply chain attacks, which compromise third-party integrations.
The best solutions are implementing Extended Detection and Response tools for real-time threat detection, Zero Trust Architecture to limit access, and AI threat intelligence platforms to stay aware of potential security threats. Regular cloud penetration testing is also essential, as it can reveal vulnerabilities before it’s not too late.
Another key challenge worth mentioning is budgetary constraints. Unfortunately, in many cases, cost optimization happens at the expense of security, which leads to increased risk. Therefore, to effectively address these challenges, organizations must invest in education, tools, and resources that enable a balanced approach to improved cloud security. – Julia Chotkiewicz, Cloud Security Engineer
How To Build a Cloud Security Strategy Step-by-Step?
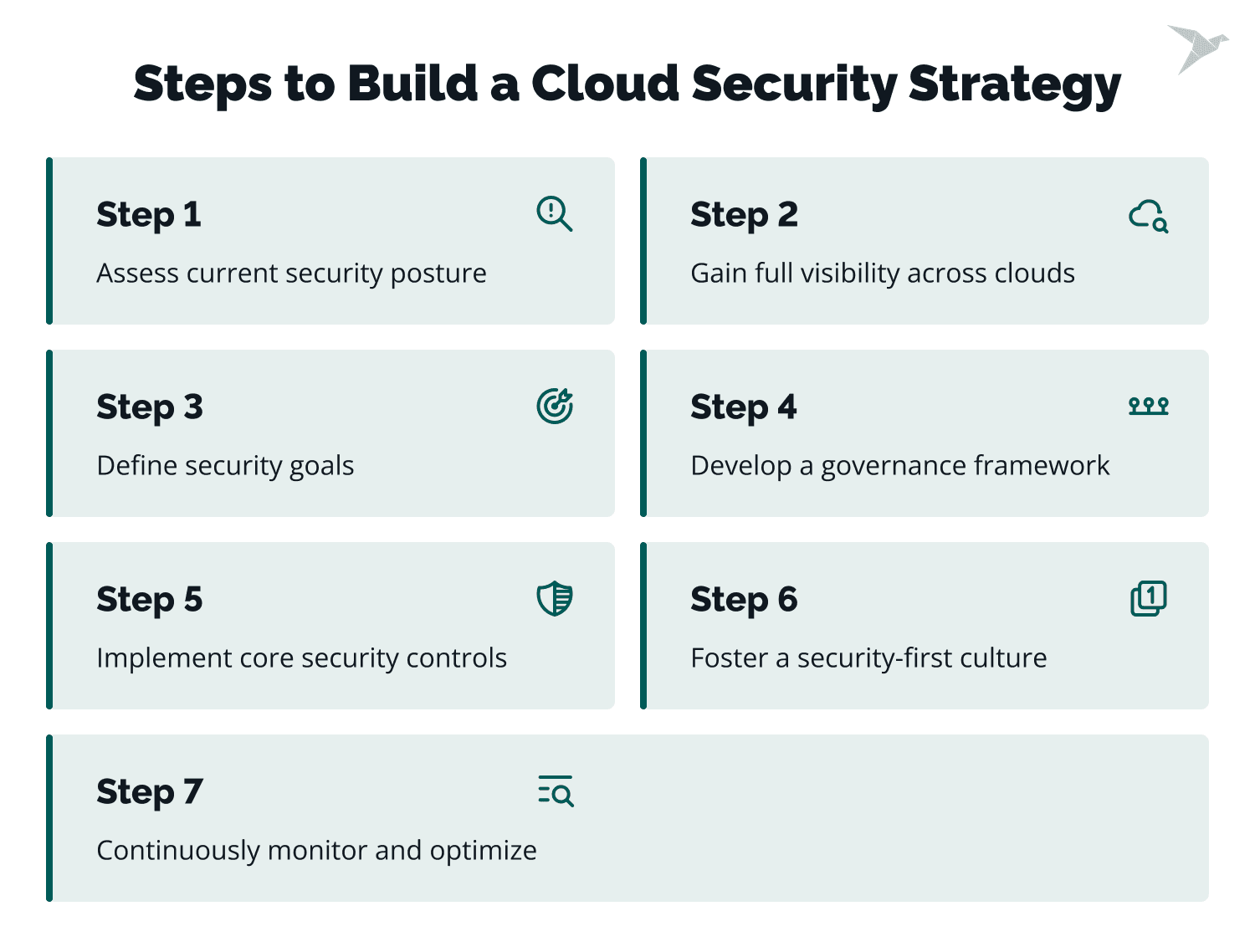
You build a cloud security strategy by moving from visibility to control, then from control to continuous improvement. Each step builds on the previous one to reduce risk without slowing cloud operations. Below is the detailed plan on how to build a successful cloud security strategy:
Step 1: Assess current security posture
The foundation of implementing a cloud security strategy begins with understanding where you stand. Conduct a comprehensive security audit to estimate configurations, weaknesses, and compliance gaps. This step helps you identify where real risk exists today, not where you assume it might be.
Such tools as Prowler, AWS Security Hub, Azure Security Center, or Google Cloud Security Command Center can help you spot misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. You can also simplify the process by utilizing commonly used sets of checks like CIS benchmarks to ensure that you have covered checks for most of the best practices for cloud security. For example, if a public-facing storage bucket lacks encryption, it must be marked for urgent improvement.
Additionally, create a risk map for the cloud assets that are crucial to your business to prioritize your response. For example, protecting customer data stored in a cloud database has a higher priority than protecting archived logs. This prioritization prevents security teams from spending time on low-impact issues while critical exposures remain open.
Step 2: Gain full visibility across clouds
Without full visibility across cloud environments, organizations may miss blind spots that could lead to security breaches. A good idea is to use CSPM tools like Prisma Cloud, Lacework, or Microsoft Defender for Cloud. With them, you can get a unified view across all cloud environments. Visibility is also critical in cloud environments because assets can be created, modified, or deleted without centralized tracking.
Such tools as AWS VPC Flow Logs, Azure Network Watcher, or GCP Traffic Director effectively track and analyze traffic between cloud resources for unusual patterns. Additionally, cloud-native logging tools like AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Logging are useful for monitoring user activity, API calls, and system events.
For instance, an organization using AWS for storage, Azure for hosting applications, and GCP for machine learning workloads can use CSPM to track configuration changes in all cloud environments.
Step 3: Define security goals
For the third step, set clear, measurable goals that are in line with your business objectives and compliance requirements. They should cover aspects such as incident response time, data protection, and governance. Clear goals make security measurable and actionable, rather than just an abstract ideal.
Here are some example objectives:
- Achieve compliance with CIS benchmarks v1.4 in not more than six months using tools like AWS Security Hub or Azure Policy.
- Shorten average response time to security incidents by 20% using automated tools such as AWS Lambda for automated incident mitigation.
- Achieve 100% encryption of confidential data across all cloud services within three months.
All goals should include success metrics, such as achieving SOC 2 Type II certification for cloud-hosted environments to gain customer trust. Without defined metrics, it becomes difficult to prove progress or justify security investments.
Step 4: Develop a governance framework
Next, make a data governance framework that specifies roles, responsibilities, and workflows for security management and aligns cloud operations with security policies. This is necessary to keep all teams consistent and accountable. Governance ensures that security decisions are repeatable and not dependent on individual judgment. For this, define role-based responsibilities for teams such as DevOps, IT, and compliance.
It is essential to set cloud-specific policies. For example, the requirement that any new cloud deployment must undergo an automated security audit using Infrastructure as Code tools such as Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to automatically achieve compliance standards. Additionally, consider implementing centralized dashboards from tools like Prisma Cloud or Prowler Pro to reach visibility and establish policies across multi-cloud environments.
All the above-mentioned governance practices reduce the risk of security gaps caused by inconsistent deployment practices.
Step 5: Implement core security controls
This step makes strategy enforceable through concrete controls. Here, you need to deploy and integrate the basic security measures that form the core of cloud security. These controls include IAM, encryption, network security segmentation, and real-time monitoring.
We’ve described some of the security controls in the previous section, but let’s recall some important examples:
- The usage of IAM tools like AWS IAM Access Analyzer to detect overly permissive or unused resources and enable least-privilege access. For instance, only the finance team can access financial systems to reduce exposure to insider threats.
- Implementing encryption at rest and in transit. For example, ensuring sensitive data is stored with AES-256 encryption and transmitted using TLS 1.3 protocols.
- Network segmentation to isolate workloads. For instance, separate development, testing, and production environments to prevent lateral movement in case of a breach.
- The usage of cloud-native monitoring tools like AWS CloudTrail to track access logs and spot anomalies.
Based on my experience conducting AWS Well-Architected Reviews with various clients, I think organizations often neglect additional security measures, such as access control, activity monitoring, or data encryption. To avoid this mistake, companies should conduct configuration audits to ensure their settings align with actual security needs. It’s important to adjust default settings to meet the specific requirements of the organization, for example, by restricting access and enabling data encryption, both at rest and in transit (it's best to take advantage of the built-in encryption features offered by cloud platforms). – Julia Chotkiewicz, Cloud Security Engineer
Step 6: Foster a security-first culture
The human factor plays a vital role in cloud security. Building a proactive security culture is necessary for minimizing human errors, which are often the main reason for security breaches. Technical controls are far less effective when people don’t understand how their actions affect cloud security. This step makes security part of daily workflows rather than a separate task.
For this, regularly educate employees on phishing, secure coding practices, and compliance standards. Platforms like KnowBe4 or Cybersecured.team offer interactive security training.
Don’t forget to reward employees for spotting security risks, such as noticing a phishing email, to encourage awareness. Additionally, you can implement security checks for cloud-hosted applications into development workflows. For example, mandate code scans for vulnerabilities before deployment using tools like Snyk together with AWS CodePipeline.
Step 7: Continuously monitor and optimize
The last but not the least step refers to ongoing monitoring and optimization. Cloud security is not static, so it must adapt to deal with new threats, technologies, and business needs. Constant monitoring and optimization help keep your defenses effective. This step ensures the strategy stays relevant as cloud usage evolves.
Here are some example practices:
- Implementing behavioral analytics tools like Splunk to identify unusual activity, such as a user logging in from an unexpected location or device.
- Regular updates of security configurations using CSPM tools like Prisma Cloud to discover deviations from best practices for cloud security.
- Conducting penetration testing (every six months) to identify vulnerabilities before they are compromised.
- Automating threat responses with SOAR tools to ensure that incidents like unauthorized access attempts are quickly resolved.
It's important to remember that the selection of specific tools should be based on the organization's individual needs and capabilities. What matters most is understanding that effective security is a combination of the right cloud technologies, processes, and a conscious approach by the entire team. – Julia Chotkiewicz, Cloud Security Engineer
How TechMagic Can Help With a Cloud Security Strategy
It’s common for cloud security to lose clarity as infrastructure scales and responsibilities spread. That’s where an experienced security partner helps.
TechMagic provides expert assistance in consulting, building, and implementing a cloud security strategy that fits how your cloud is actually used. We don’t start with generic policies. We start with your environment, your risks, and the decisions your people make every day, and define clear controls your organization can apply and sustain.
Here’s what you get when you work with us:
- A clear security baseline for your cloud environments, so you know what “secure” means in practical terms
- Actionable fixes for high-risk misconfigurations and access issues, prioritized by impact
- Security guidance that supports delivery speed instead of blocking it
- A repeatable cloud security workflow your internal owners can follow, audit, and improve over time
- Clear documentation and handoff, so security doesn’t depend on a few key people
If you want to reduce risk without slowing the business, let’s talk. Book a meeting, share a bit about your cloud setup and constraints, and we’ll outline the safest path forward.

Wrapping Up and What’s Next for Cloud Security
A comprehensive cloud security strategy roadmap is a must-have for organizations today. It helps protect assets within a company in a unified way and achieve compliance. For CEOs and managers, it is vital to focus on core pillars, address key challenges, and follow structured steps to keep your company resilient against threats.
In this guide, we covered what a cloud security strategy is, why it matters for modern businesses, the core pillars that make it effective, the most common roadblocks, and a practical step-by-step approach you can apply in real environments. If you need a faster starting point, a solid cloud security strategy template can help you align stakeholders and document decisions, but it still needs to reflect your actual cloud setup and risks.
Looking ahead, cloud environments will only become more distributed, automated, and interconnected, which means small configuration mistakes will carry more impact. At the same time, expectations for security evidence and response readiness will rise, and organizations that treat cloud security as an operating discipline will have a clear advantage.
FAQ

What is a cloud security strategy?
A cloud security strategy is a detailed framework with policies, practices, and technologies designed to protect cloud systems, apps, and data against threats. It clarifies who can access what, how data is protected, what gets monitored, and how incidents are handled. A good cloud security strategy example is an organization that enforces least-privilege access, encrypts sensitive data by default, monitors critical events centrally, and runs regular recovery tests to prove it can respond under pressure.
What are the cloud strategies?
Cloud strategies refer to plans for adopting, managing, and protecting cloud environments. They typically cover which workloads go to the cloud, how to control cost and performance, and how to manage risk across services and providers. In practice, most organizations use a mix of cloud security strategies depending on workload sensitivity, compliance requirements, and operational maturity.
What are the methods of cloud security?
The main methods are implementing effective IAM and advanced security tools, data encryption, ensuring compliance with regulations, creating a security-first culture, and continuous monitoring. Strong best practices for cloud security also include secure configuration baselines, consistent logging, routine access reviews, and regular testing of incident response and recovery.
How to build a successful cloud security strategy?
To build a successful cloud security strategy, start with an assessment of your current posture, then improve visibility across environments, define measurable security goals, establish governance, and implement core controls such as IAM, encryption, segmentation, and monitoring. The strategy should be revisited regularly as cloud services, usage patterns, and threats evolve, so it stays practical and effective.
How do you secure a multi-cloud environment?
Securing a multi-cloud environment starts with consistency. Organizations need shared security standards across providers, centralized visibility, and clear ownership of identities, data, and configurations. Using CSPM and SIEM tools helps detect misconfigurations and suspicious activity across platforms, while standardized IAM, encryption, and logging policies reduce gaps that attackers often exploit when security differs between clouds.
Is cloud security different for regulated industries?
Yes, cloud security is more demanding for regulated industries because security controls must align with specific legal and compliance requirements. Healthcare, finance, and other regulated sectors must enforce stricter access controls, stronger encryption, detailed audit logging, and clear data handling rules. Cloud security strategies in these environments focus not just on protection, but on proving compliance through continuous monitoring and documented controls as well.

 Software Development
Software Development Security Services
Security Services Cloud Services
Cloud Services Other Services
Other Services















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy