AI in Clinical Data Management: How It Works and Why It Is Effective
Last updated:27 January 2025
Clinical trials generate vast amounts of data. According to the World Health Organization, only the USA conducted almost 6,000 clinical trials in 2024 and 186,497 over the last 25 years. Managing all this data precisely and efficiently is essential for medical research to progress.
Traditional methods often fail to cope with the scope and complexity of modern clinical data. This leads to inefficiency, delays, and potential errors. Luckily, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has come to the rescue and become a solution for efficient clinical data management. How? Keep reading to find out.
Key Takeaways
- The data demands in clinical trials are rising every day. That’s why efficient clinical data management (CDM) is essential – to ensure precision, compliance, and progress in medical research.
- Common issues preventing trial efficiency in CDM include managing large, complex datasets, maintaining regulatory compliance, ensuring data security, and reducing manual errors.
- AI technologies can address key CDM challenges. They automate data cleaning, improve integration, and enable predictive analytics.
- AI improves data quality, reduces timelines and costs, facilitates informed decisions, and smoothly handles growing data volumes.
What Is Clinical Data Management?
Clinical data management (CDM) refers to collecting, cleaning, and organizing data from clinical trials. CDM aims to enable high-quality, reliable information for regulatory submissions and decision-making. It ensures that data is precise, full, and compliant with necessary standards. The clinical data management processes cover various tasks, including:
- Database design. Creating databases that can efficiently store and retrieve clinical trial data.
- Data entry and validation. Ensuring accurate entry and verifying the consistency and integrity of data.
- Data cleaning. Identifying and resolving errors or inconsistencies in the dataset.
- Statistical analysis and reporting. Data analysis to gain insights and provide reports for regulators.
Many organizations also use trial software to streamline these CDM processes and allow teams to manage clinical data more efficiently from collection to final reporting.
Current Market Size and Its Growth
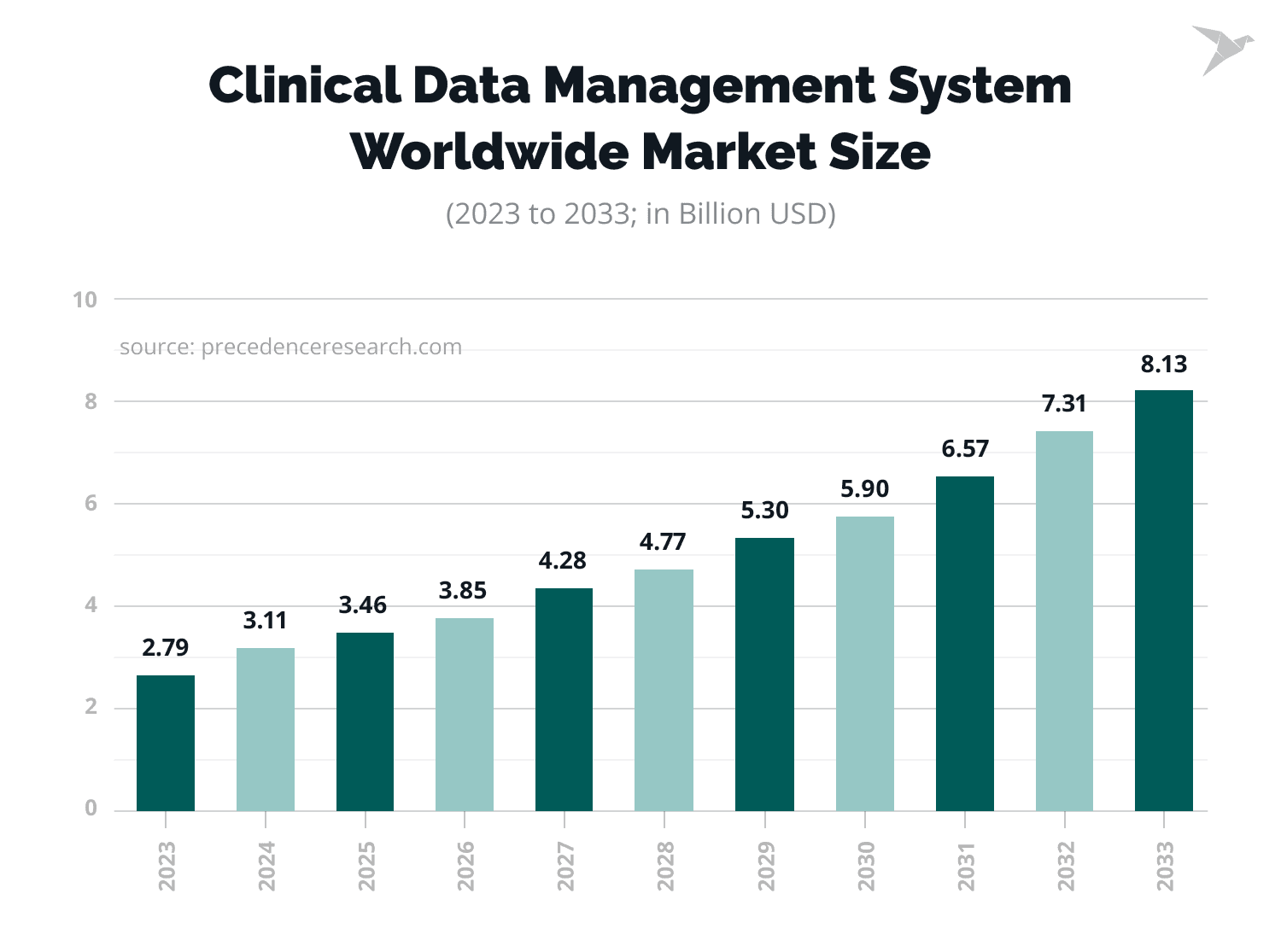
The growing demand for clinical data management services is reflected in statistical figures. The clinical data management market size was estimated at $3.11 billion in 2024. It is expected to reach $8.13 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 11.28% from 2024 to 2033.
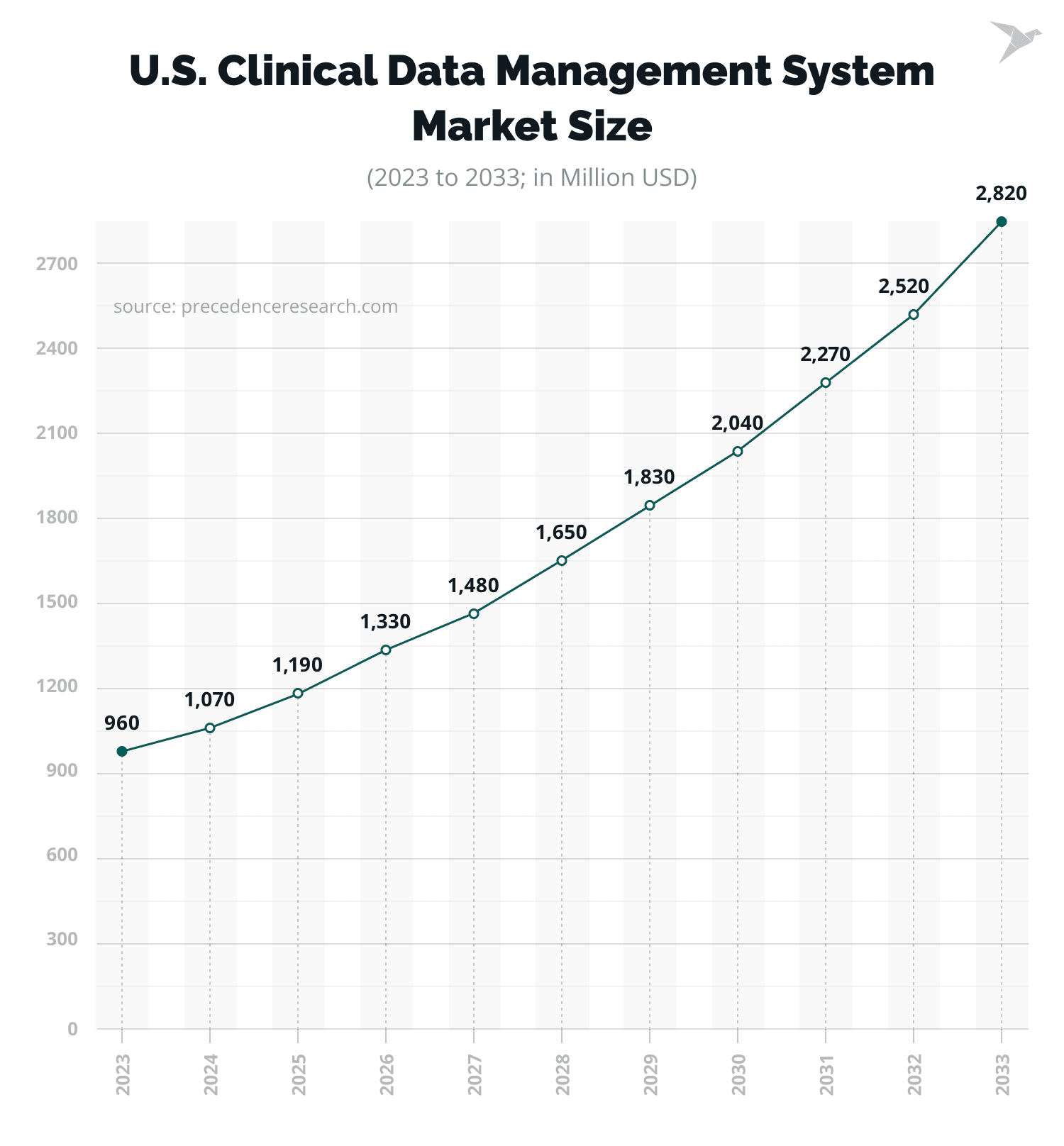
At the same time, the clinical data management market size in the USA alone was assessed at $1,070 million in 2024. According to the predictions, it is expected to reach $2,820 million by 2033, at a CAGR of 11.37% from 2024 to 2033.
Let’s now explore the key challenges clinical data managers and other involved parties often face.
Common Challenges in Clinical Data Management
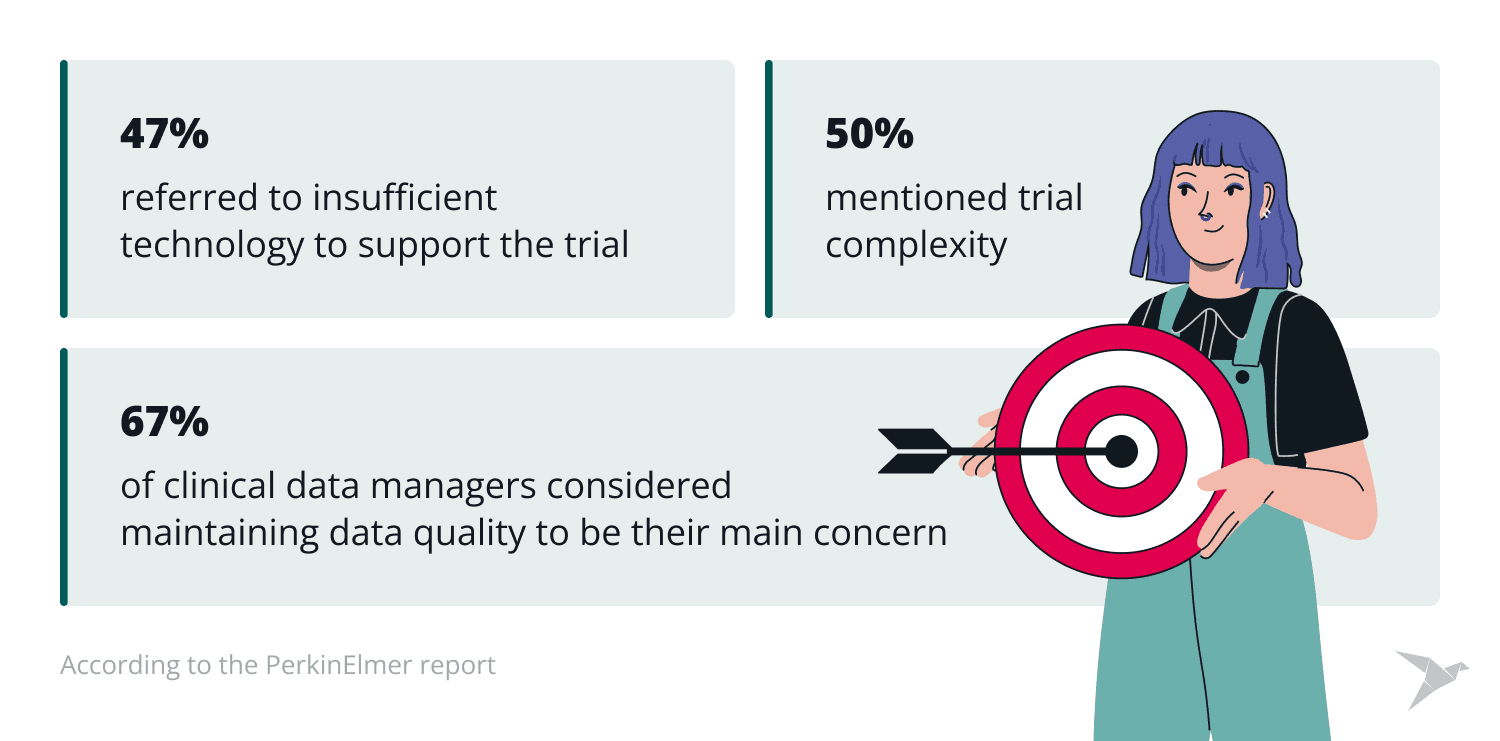
Despite its importance, CDM faces challenges that can hinder the productivity and accuracy of clinical trials. According to the PerkinElmer report, 63% of clinical data managers considered maintaining data quality to be their main concern, 50% mentioned trial complexity, and 47% referred to insufficient technology to support the trial.
Let’s read about these and more hurdles of clinical data management in detail!
Data volume and complexity
Today, clinical trials produce large datasets involving structured data (e.g., lab results) and unstructured data (e.g., physician notes, imaging data). The heterogeneity of data formats often causes difficulties in integration. For example, reconciling data from wearable devices with lab results can require significant manual effort.
Time and cost constraints
The processes of manual data management are labor-intensive, expensive, and time-consuming. A Tufts CSDD Impact report focused on clinical trial budgets and concluded that average budgets exceed $65 million for Phase III oncology protocols and $54 million for non-oncology protocols. The report also emphasized that protocol design complexity and data volume increased, which can contribute to higher data management costs.
Human error
Manual data entry and cleaning can cause errors that can affect the validity of clinical trial results. For instance, transcription errors in data entry can lead to anomalies that impact statistical analysis and results.
Regulatory compliance
Maintaining compliance with regulatory standards can be difficult without automated tools. Non-compliance can lead to trial delays, fines, or even trial termination. An Oracle survey showed that 81% of respondents recognized data governance as the main challenge in reaching regulatory compliance for clinical trial data.
Integration challenges
Clinical trials often include data from multiple sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, and lab systems. Harmonizing these multiple data streams is hard. For example, a multi-site trial involving international collaborators may face difficulties due to varying data and regulatory standards.
Data security
Protecting confidential patient data while still allowing authorized personnel to access it is another significant concern. According to Statista, the healthcare sector is thought to be one of the most vulnerable industries to cybercrime. Moreover, this sector had the highest average data breach cost in recent years, at nearly $11 million. Thus, implementing robust security measures is vital.
Delayed decision-making
Slow data processing and analysis can lead to delays in making decisions during trials. For instance, detecting adverse events in real-time is critical, but traditional methods may lag in detecting and reporting such events.
Resource limitations in smaller organizations
Small and medium-sized research organizations often have limited resources for implementing effective CDM practices. This can lead to inefficiencies and potential data quality issues. Compared to large companies, these organizations may rely on legacy systems that are poorly equipped to deal with modern data requirements.
Data gaps in patient recruitment and retention
Insufficient data integration during patient recruitment leads to ineffective trial designs. For example, in rare disease trials, it is often difficult to quickly find appropriate patients due to fragmented data sources, which can delay the start of a trial.
The good news is that AI can address all these challenges. Let’s see how it is possible!
Practical Applications of AI in Clinical Data Management
AI technologies, including machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and robotic process automation (RPA), help solve the challenges in CDM processes described above effectively.
In many cases, these tools take the form of intelligent AI agents that can autonomously perform tasks such as data validation, integration, monitoring, and reporting across clinical trial systems.
Here are key points of how AI is used in CDM workflows:
AI tools for data cleaning and validation
AI tools identify errors, such as duplicate entries or missing values, with greater precision than manual methods. For example, AI algorithms can enhance data cleaning processes in clinical trials. Such tools can flag missing lab results or incorrect patient identifiers, which improves the process of preparing datasets for analysis.
AI for predictive analytics
ML models can predict patient recruitment rates, foresee dropout risks, and detect potential adverse events. Thus, trial design and execution processes can be optimized. For example, a big pharmaceutical company can implement predictive analytics to find optimal site locations for a global trial, which will reduce recruitment time.
If you are looking for professional healthcare software development services, experts at TechMagic are always here to help you develop a unique healthcare solution.
NLP for unstructured data
NLP can be applied to improve the process of dealing with data in clinical data management. AI can extract necessary insights from unstructured data sources, such as clinical notes, pathology reports, and imaging data.
For instance, an organization can use NLP to analyze oncology-related EHR data. This can enable insights into patient treatment outcomes, improve decision-making, and help choose the most effective treatment practices. Examples of effective NLP tools include AWS Comprehend Medical and Clinithink CLiX.
Solutions like AWS Comprehend Medical are part of the broader suite of AWS for healthcare offerings, which support secure, scalable, and AI-driven data analysis in clinical environments.
Additionally, advanced tools like large language models (LLMs) can be leveraged for data transformation tasks. For example, LLMs can convert complex medical notes into interoperable standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), as demonstrated by Tiro Health.
AI for integration and interoperability
Data volume and complexity are two of the main challenges during clinical trial management processes. Using AI tools in CDM is a great idea, as they can simplify the integration of data from multiple sources. AI can ensure smooth data flow and consistency of data. For example, healthcare organizations can use AI tools to integrate patient data from EHRs and imaging systems and enable comprehensive analyses of patient health.
AI for regulatory compliance and audit readiness
Automated AI tools are great helpers in CDM for monitoring compliance with regulatory standards. How do they work? They scan the system and flag potential issues. For example, a company can use AI to ensure adherence to GDPR requirements, thus reducing audit preparation time.
AI for risk-based monitoring
AI recognizes high-risk data points that need to be more thoroughly reviewed, which allows for more targeted and efficient monitoring. For instance, AI tools can prioritize the review of adverse event reports from sites with higher error rates.
AI for adaptive trial designs
AI supports adaptive trial designs by analyzing incoming data. For example, in a phase II trial for a rare genetic disorder, AI can identify early efficacy signals and allow for the expansion of patient recruitment into specific subgroups.
AI for patient matching and recruitment
AI algorithms analyze data from patient records and trial eligibility criteria to choose suitable candidates more efficiently. For instance, AI-driven solutions can speed up recruitment timelines as they use predictive models to match patients with trials based on historical data, which saves time.
AI for automated reporting
AI produces real-time reports and visualizations, which simplifies the process of sharing trial progress with stakeholders. For example, a biopharma company that uses AI to automate safety reporting can significantly cut the time needed for regulatory submissions.
Learn about our expertise in the industry and what we have to offer

Benefits of AI in clinical data management
So, let’s summarize the key benefits of implementing AI in medical data management:
- AI improves data quality. AI algorithms can automatically detect anomalies, inconsistencies, and outliers in datasets, ensuring higher data quality.
- AI reduces timelines. Automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and validation, significantly reduces processing time and speeds up clinical trials.
- AI cuts expenses. AI tools optimize operations and reduce manual effort, which lowers operational costs.
- AI helps with informed decision-making. AI enables comprehensive data analysis, which provides practical intelligence for trial optimization and informed decisions.
- AI can handle bigger volumes of data. AI systems cope with the increasing volume and complexity of data without compromising performance.
The demand for AI in the healthcare industry is reflected in statistics. The global AI in healthcare market size is forecasted to grow from $26.69 billion in 2024 to about $613.81 billion by 2034.
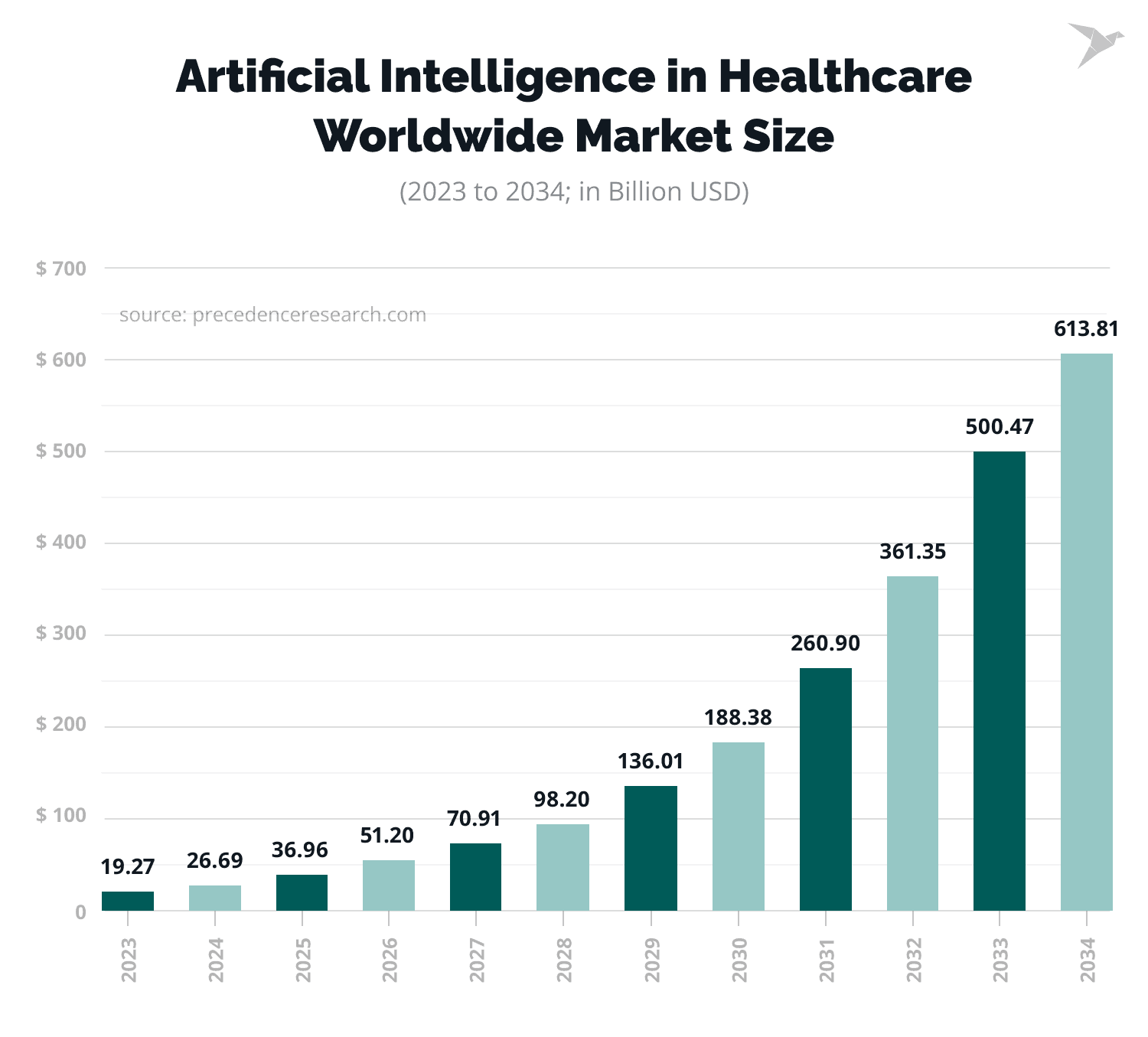
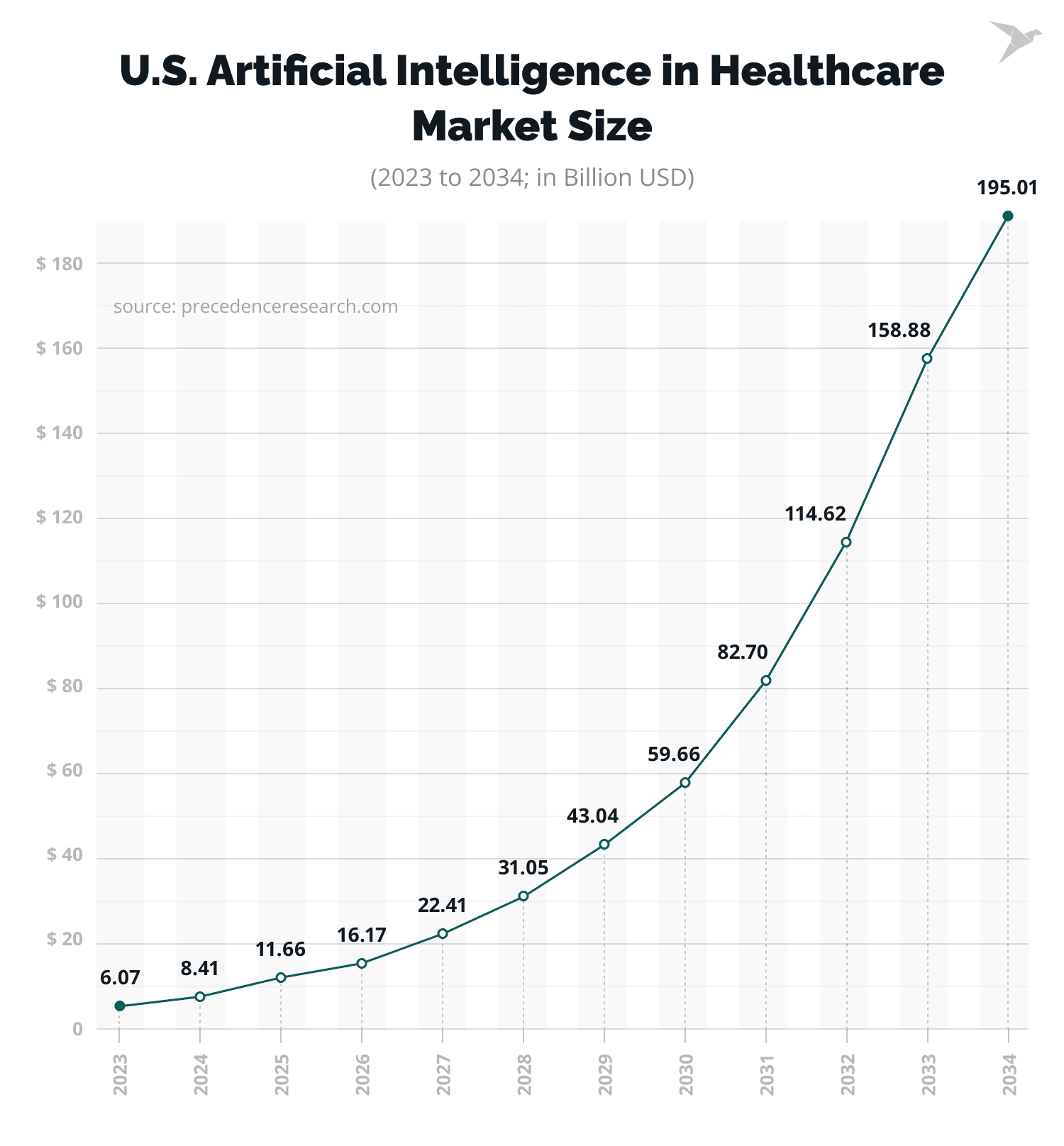
At the same time, the AI in healthcare market size in the USA was $8.41 billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach about $195.01 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 37% from 2024 to 2034.
How to Overcome Fears and Employee Resistance to AI Adoption
Adopting AI in clinical data management often comes with challenges, with resistance from employees being one of the main ones. They typically worry due to the potential for certain positions to be replaced or redefined by AI. Such concerns often appear because of the lack of understanding or wrong opinions about AI and ML and how they work. The solution to dispelling fears and misunderstandings lies in raising stakeholders’ awareness of AI – how it functions and how it can enhance operations and clinical trial processes and improve patient outcomes.
A comprehensive approach to addressing these concerns involves promoting awareness and comprehension through an effective training strategy:
Raising AI awareness
Developing AI literacy is essential to easing fears and ensuring successful adoption. Educating teams can help companies build trust and confidence in AI.
To achieve this, we recommend structured AI training. These can include online courses, workshops, and a dedicated knowledge base to provide accessible information about AI concepts. When raising awareness, it is essential to use real-world examples. Demonstrations and case studies can illustrate how AI solutions have driven positive outcomes in clinical data management.
It is important to highlight AI’s ability to learn. Help teams understand that AI continuously learns and improves. Emphasize its collaborative potential rather than competition with human roles. Additionally, we suggest encouraging the exploration of new use cases. Facilitate brainstorming sessions to identify potential applications of AI in specific workflows or challenges.
Bring clinical data managers into the AI workflow
For AI adoption to be effective, clinical data managers must feel they have an active role in shaping how AI is implemented. This can be achieved by establishing structured channels for data managers to provide insights and critiques on AI systems. It is also essential to explain how human input enhances AI performance and how AI evolves based on real-world data.
Additionally, we recommend providing transparency on common AI challenges, such as biased datasets or incomplete data, and discussing strategies to mitigate these issues.
Proactively encourage change
Change management plays a vital role in overcoming resistance and ensuring smooth integration of AI. Communicate the long-term benefits of AI, such as reduced workload and enhanced efficiency, to counter fears of redundancy.
A good idea is to give teams practical experience using AI tools to increase familiarity and comfort levels. Additionally, we recommend opening forums where employees can voice concerns, ask questions, and receive direct answers.
Importantly, ensure that human control is maintained in key decision-making processes to minimize the risks associated with automation. If your organization requires competent EHR/EMR software development services, experts at TechMagic can develop an efficient and innovative healthcare solution tailored to your business needs.
Addressing Data Privacy Concerns in AI Adoption
When implementing Artificial Intelligence in clinical data management, it is vital to prioritize and dedicate resources to data privacy and security. Sensitive patient information must be protected to comply with regulations. Trust in AI systems depends on proactive steps to protect data.
Key considerations for data privacy are the following:
- Avoid sharing patient data with OpenAI or similar platforms. Refrain from sharing sensitive clinical or patient data unless explicit safeguards are in place.
- Data anonymization. Anonymize patient data before feeding it into AI systems to prevent identification.
- Regulatory compliance. Ensure all AI applications adhere to relevant data protection regulations through regular audits.
- Controlled access. Limit access to patient data to authorized personnel using role-based permissions.
- Vendor transparency. Review AI vendors’ data handling policies to confirm they do not share or misuse patient data.
- Data encryption. Use robust encryption protocols to secure data in transit and at rest.
The Future of AI in Clinical Data Management
The usage of AI for clinical data management is still in its early stages, but the future of this is promising. Key future trends of AI in hospital data management include:
- Federated learning which enables AI models’ training on decentralized data without compromising patient privacy and providing cross-institutional collaboration.
- Using AI together with blockchain technology to strengthen data security and foster trust in clinical data management.
- Smart AI predictive models that contribute to personalized trial designs and optimize treatments for individual patients.
- Global collaboration, which means that AI can bridge the gap between geographically dispersed teams and enable seamless collaboration for data sharing across borders.
- Advanced NLP tools which enable the smooth integration of unstructured data, such as patient-reported outcomes and physician notes.
- AI-augmented decisions, which combine AI insights with human expertise and lead to more informed decisions, improving trial success rates.
Wrapping Up
Using AI in clinical data management marks a new era of clinical trials. AI can address a wide range of challenges and present new opportunities for efficiency, precision of data, and innovation. Of course, barriers to adoption still remain, but a strategic approach that prioritizes education, collaboration, and data security can help organizations harness the best of AI.
It is obvious that AI will play a key role in changing the industry of clinical trials and advancing medical research. The path forward lies in understanding and accepting the fact that AI is not a replacement for human expertise, but a powerful tool that complements and facilitates clinical research efforts.
Experts at TechMagic can help you develop a unique AI solution, so don’t hesitate to contact us!

FAQ

How is AI used in clinical data management?
AI automates tasks such as data cleaning, integration, and predictive analytics, which reduces errors, speeds up processes, and improves data quality.
How is AI used in healthcare data?
AI processes non-structured data from sources like medical imaging and patient records, detects disease patterns using ML, and enables real-time monitoring for proactive healthcare interventions.
How is AI used in EHR?
AI simplifies EHR workflows. For example, AI can convert voice notes into structured data, detect potential medication errors, and generate custom treatment suggestions based on patient history.
What is clinical data management, and why is it important?
Clinical data management involves clinical trial data collection, cleaning, and organization. It aims to provide reliable insights for regulatory decision-making and contribute to the development of medical research.
What are the benefits of using AI in the processes of clinical data management?
AI improves data quality, cuts operational costs, and speeds clinical trials as it automates repetitive tasks. It also facilitates informed decision-making with advanced analytics and handles large data volumes without compromising precision.

 Software Development
Software Development Security Services
Security Services Cloud Services
Cloud Services Other Services
Other Services















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy